afterLoad (456.22KB) (3.86ms)
afterInitialise (1.27MB) (85.77ms)
afterRoute (840.55KB) (25.07ms)
beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.75KB) (374μs)
afterRenderComponent com_tags (3.63MB) (426ms)
afterDispatch (27.44KB) (4.84ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (423.86KB) (17.66ms)
Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (1.68ms)
After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (837μs)
Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (25μs)
After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (55μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (5.54KB) (189ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (30μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (222μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (16μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (18.22KB) (153ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (43μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (85μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (25μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (10μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (19μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (8μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (19μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (8μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (17μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (3.74ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (42μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (396μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (18μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (1.55ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (34μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (56μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (3.93ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (55μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (86μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (13μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (31μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (381μs)
afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (46μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (14μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (26μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (25μs)
afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (25μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (11μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (49μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (11μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (24μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (12μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (29.14KB) (729μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (190.95KB) (1.64ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (73μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (20μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (22.41KB) (2.06ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (26μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (15μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (3.12ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (7μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (319μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (184μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.64KB) (1.42ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (71μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (152μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (1.04ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (68μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (22μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (954μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (42μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (12μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (1.12ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (7μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (68μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (217μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (198μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (29μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (89μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (97μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (122μs)
afterRender (771.02KB) (15.19ms)
| 1 x afterRenderComponent com_tags (3.63MB) (44.79%) | 425.50ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (5.54KB) (19.93%) | 189.35ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (18.22KB) (16.15%) | 153.41ms |
| 1 x afterInitialise (1.27MB) (9.03%) | 85.77ms |
| 1 x afterRoute (840.55KB) (2.64%) | 25.07ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (423.86KB) (1.86%) | 17.66ms |
| 1 x afterRender (771.02KB) (1.6%) | 15.19ms |
| 1 x afterDispatch (27.44KB) (0.51%) | 4.84ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (0.41%) | 3.93ms |
| 1 x afterLoad (456.22KB) (0.41%) | 3.86ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (0.39%) | 3.74ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (0.33%) | 3.12ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (22.41KB) (0.22%) | 2.06ms |
| 1 x Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (0.18%) | 1.68ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (190.95KB) (0.17%) | 1.64ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (0.16%) | 1.55ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.64KB) (0.15%) | 1.42ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (0.12%) | 1.12ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (0.11%) | 1.04ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (0.1%) | 954μs |
| 1 x After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (0.09%) | 837μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (29.14KB) (0.08%) | 729μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (0.04%) | 396μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (0.04%) | 381μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.75KB) (0.04%) | 374μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (0.03%) | 319μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (0.02%) | 222μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (0.02%) | 217μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (0.02%) | 198μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (0.02%) | 184μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (0.02%) | 152μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (0.01%) | 122μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (0.01%) | 97μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (0.01%) | 89μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 86μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (0.01%) | 85μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (0.01%) | 73μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (0.01%) | 71μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 68μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (0.01%) | 68μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (0.01%) | 56μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (0.01%) | 55μs |
| 1 x After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (0.01%) | 55μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (0.01%) | 49μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (0%) | 46μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (0%) | 43μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (0%) | 42μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (0%) | 42μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (0%) | 34μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (0%) | 31μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (0%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (0%) | 29μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (0%) | 26μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (0%) | 26μs |
| 1 x Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (0%) | 25μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (0%) | 25μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (0%) | 25μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (0%) | 25μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (0%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (0%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (0%) | 17μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (0%) | 16μs |
| 3 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (0%) | 16μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (0%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (0%) | 14μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (0%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (0%) | 6μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (0%) | 5μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (0%) | 2μs |
 According to the statistics, far too many patients contract an infection while being hospitalized in a Danish hospital. This has enormous human and economic costs that need to be addressed. Hospital infections are not only a consequence of poor hygiene, it actually turns out that 40 percent of the patients are malnourished to some degree, which impairs their immune system and makes them an easier target for infections. Lack of vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium, zinc, and iron seem to be the big and overlooked problem.
According to the statistics, far too many patients contract an infection while being hospitalized in a Danish hospital. This has enormous human and economic costs that need to be addressed. Hospital infections are not only a consequence of poor hygiene, it actually turns out that 40 percent of the patients are malnourished to some degree, which impairs their immune system and makes them an easier target for infections. Lack of vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium, zinc, and iron seem to be the big and overlooked problem.







 Even if you eat a healthy and balanced diet, it can be difficult to get enough
Even if you eat a healthy and balanced diet, it can be difficult to get enough  According to a new study from Johns Hopkins University in the United States,
According to a new study from Johns Hopkins University in the United States, 
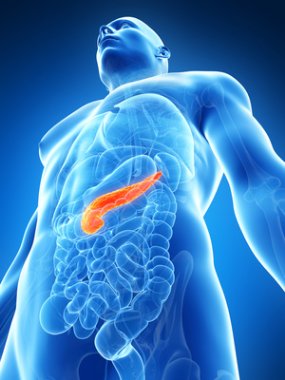 A new American study shows that chronic alcohol abuse impairs the ability of the pancreas to absorb
A new American study shows that chronic alcohol abuse impairs the ability of the pancreas to absorb 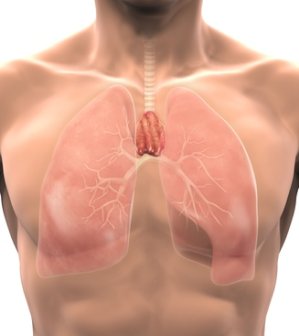 Even the earliest ageing processes are known to damage central parts of our immune system, leaving us more exposed to infection, inflammation, and cancer. However, new studies demonstrate that antioxidants such as
Even the earliest ageing processes are known to damage central parts of our immune system, leaving us more exposed to infection, inflammation, and cancer. However, new studies demonstrate that antioxidants such as  It is estimated that one billion people worldwide lack
It is estimated that one billion people worldwide lack 
 Melanoma is a type of malignant skin cancer that spreads rapidly. Being vitamin D-deficient doubles the risk of dying of the disease, according to a Spanish study that was presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology congress. It is commonly known that sunburns, which one should generally avoid, increase the risk of contracting skin cancer. But we must not forget that the summer sun is our main source of
Melanoma is a type of malignant skin cancer that spreads rapidly. Being vitamin D-deficient doubles the risk of dying of the disease, according to a Spanish study that was presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology congress. It is commonly known that sunburns, which one should generally avoid, increase the risk of contracting skin cancer. But we must not forget that the summer sun is our main source of 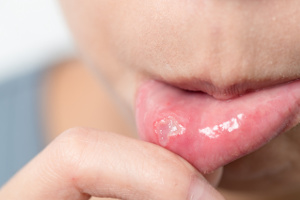 Around 25 percent of adults have had canker sores, also referred to as recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). The condition is characterized by painful, superficial sores, and we don’t know all that much about what causes it or how to treat it. However, according to a meta-analysis that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, a possible cause may be low blood levels of
Around 25 percent of adults have had canker sores, also referred to as recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). The condition is characterized by painful, superficial sores, and we don’t know all that much about what causes it or how to treat it. However, according to a meta-analysis that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, a possible cause may be low blood levels of 
 The coronavirus has spread from Wuhan in China to a number of continents, where it has caused massive fear and affected daily life and the global economy. Although most people that get the infection experience a mild course of events, the greatest fear is the potentially life-threatening complications in the respiratory system caused by oxidative stress, which have already taken thousands of human lives. Chinese scientists now call for early intravenous therapy with large doses of vitamin C to prevent oxidative stress and the life-threatening complications that follow in the wake of a derailed immune system. Many researchers also claim that higher intake of vitamin C from dietary sources or supplements help prevent by boosting and regulating the immune system in the upper respiratory tract. The same goes for vitamin D and selenium.
The coronavirus has spread from Wuhan in China to a number of continents, where it has caused massive fear and affected daily life and the global economy. Although most people that get the infection experience a mild course of events, the greatest fear is the potentially life-threatening complications in the respiratory system caused by oxidative stress, which have already taken thousands of human lives. Chinese scientists now call for early intravenous therapy with large doses of vitamin C to prevent oxidative stress and the life-threatening complications that follow in the wake of a derailed immune system. Many researchers also claim that higher intake of vitamin C from dietary sources or supplements help prevent by boosting and regulating the immune system in the upper respiratory tract. The same goes for vitamin D and selenium. It has already been documented that the widespread problems with vitamin D deficiency increase the risk of being infected with COVID-19 and developing life-threatening complications. In a new study, a team of Turkish scientists has demonstrated that swift treatment with
It has already been documented that the widespread problems with vitamin D deficiency increase the risk of being infected with COVID-19 and developing life-threatening complications. In a new study, a team of Turkish scientists has demonstrated that swift treatment with 
 The summer sun is our most important source of
The summer sun is our most important source of 

 According to a new study that is published in the British Journal of Nutrition, even minor
According to a new study that is published in the British Journal of Nutrition, even minor  The most common term for this nutrient is folic acid, whereas vitamin B9 is hardly ever used. Folic acid is the synthetic form that is found in vitamin pills, while folate and folacin are the forms of the nutrient that are found naturally in food. Folic acid is very stable and gets converted into folate in the body. The vitamin is water-soluble. Most of it gets stored in the liver, which contains around half the body's total amount of folate. The nutrient is destroyed by boiling and heating.
The most common term for this nutrient is folic acid, whereas vitamin B9 is hardly ever used. Folic acid is the synthetic form that is found in vitamin pills, while folate and folacin are the forms of the nutrient that are found naturally in food. Folic acid is very stable and gets converted into folate in the body. The vitamin is water-soluble. Most of it gets stored in the liver, which contains around half the body's total amount of folate. The nutrient is destroyed by boiling and heating. Modern man is exposed to a lot of free radicals because of factors like stress, environmental toxins, etc. Free radicals are like “internal terrorists” that contribute to atherosclerosis, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and a host of other diseases. Our only protection against free radicals are antioxidants from vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds. Antioxidants work in different ways. Being deficient in a single primary antioxidant such as selenium may leave the body vulnerable to oxidative stress and disease. What most people are unaware of is that free radicals are also essential, as they are a part of our energy turnover and immune defense. The question is how do we protect ourselves the best against infections, oxidative stress, and disease? What type of antioxidant do we get from dark chocolate, green tea, coffee and red wine? How does redox therapy with vitamin C in great quantities work on cancer patients? You can read more about these topics in the following.
Modern man is exposed to a lot of free radicals because of factors like stress, environmental toxins, etc. Free radicals are like “internal terrorists” that contribute to atherosclerosis, diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, cancer, and a host of other diseases. Our only protection against free radicals are antioxidants from vitamins, minerals, and plant compounds. Antioxidants work in different ways. Being deficient in a single primary antioxidant such as selenium may leave the body vulnerable to oxidative stress and disease. What most people are unaware of is that free radicals are also essential, as they are a part of our energy turnover and immune defense. The question is how do we protect ourselves the best against infections, oxidative stress, and disease? What type of antioxidant do we get from dark chocolate, green tea, coffee and red wine? How does redox therapy with vitamin C in great quantities work on cancer patients? You can read more about these topics in the following.
 The most harmful heavy metals are mercury, cadmium, lead, nickel, and cobber, but aluminum, fluoride, iron, and calcium can also be toxic. Poisoning with heavy metals and minerals blocks other minerals such as selenium, iodine, magnesium, and zinc, all of which support numerous essential enzyme processes. At the same time, if you lack these important minerals, heavy metals are able to cause unhindered damage and increase your risk of impaired immunity, impaired fertility, autoimmune diseases, thyroid diseases, brain damage, neurological diseases, depression, hypersensitivity, etc. Chronic heavy metal toxicity is an overlooked problem, but in this article, you can read more about the subject and find out how to deal with it.
The most harmful heavy metals are mercury, cadmium, lead, nickel, and cobber, but aluminum, fluoride, iron, and calcium can also be toxic. Poisoning with heavy metals and minerals blocks other minerals such as selenium, iodine, magnesium, and zinc, all of which support numerous essential enzyme processes. At the same time, if you lack these important minerals, heavy metals are able to cause unhindered damage and increase your risk of impaired immunity, impaired fertility, autoimmune diseases, thyroid diseases, brain damage, neurological diseases, depression, hypersensitivity, etc. Chronic heavy metal toxicity is an overlooked problem, but in this article, you can read more about the subject and find out how to deal with it.
 HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, is potentially life-threatening because it attacks central cells in the immune defense. It has also been documented that HIV patients have an increased risk of lacking
HIV, the virus that causes AIDS, is potentially life-threatening because it attacks central cells in the immune defense. It has also been documented that HIV patients have an increased risk of lacking  Lack of
Lack of  Ageing is linked to uncontrolled, low-grade inflammation, also known as inflammaging, according to articles published in the journals Nature Medicine and Ageing and Disease. Although chronic inflammation is not felt directly it may set the stage for cardiovascular disease, rheumatism, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. Chronic inflammation may also cause virus infections like influenza and COVID-19 to become life-threatening because the immune defense suddenly overreacts and attacks healthy tissue. It is therefore vital for ageing people to protect themselves against chronic inflammation, which means getting plenty of vitamin D, selenium, coenzyme Q10, zinc, omega-3, and melatonin. These are all things that many older people often lack.
Ageing is linked to uncontrolled, low-grade inflammation, also known as inflammaging, according to articles published in the journals Nature Medicine and Ageing and Disease. Although chronic inflammation is not felt directly it may set the stage for cardiovascular disease, rheumatism, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. Chronic inflammation may also cause virus infections like influenza and COVID-19 to become life-threatening because the immune defense suddenly overreacts and attacks healthy tissue. It is therefore vital for ageing people to protect themselves against chronic inflammation, which means getting plenty of vitamin D, selenium, coenzyme Q10, zinc, omega-3, and melatonin. These are all things that many older people often lack. Chronic fatigue commonly follows in the wake of influenza, herpes, COVID-19, and other infections. The immune system does not function optimally, and the tiredness is caused by oxidative stress and inflammation. The condition is often accompanied by poor concentration, depression, and sleep disturbances. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between pro-inflammatory free radicals and protective antioxidants.
Chronic fatigue commonly follows in the wake of influenza, herpes, COVID-19, and other infections. The immune system does not function optimally, and the tiredness is caused by oxidative stress and inflammation. The condition is often accompanied by poor concentration, depression, and sleep disturbances. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between pro-inflammatory free radicals and protective antioxidants.  Minerals are involved in countless functions of vital importance to the immune defense. That is why lack of one or several minerals can increase your risk of infections or perhaps trigger unwanted inflammation that can damage healthy tissue. In a new review article that is published in Nutrients, a group of scientists look at magnesium, selenium, zinc, iron, and copper and their role in the immune system. They also look at the fact that vegans, older people, chronically ill, pregnant women, and elite athletes often have nutrient deficiencies that call for supplementation. The agricultural soil in Europe and many other parts of the world is selenium-depleted, which makes it challenging to get enough selenium from our diets. But it is also important not to overdose on minerals. In this article, you can read more about how to optimize your nutrient intake for your immune health.
Minerals are involved in countless functions of vital importance to the immune defense. That is why lack of one or several minerals can increase your risk of infections or perhaps trigger unwanted inflammation that can damage healthy tissue. In a new review article that is published in Nutrients, a group of scientists look at magnesium, selenium, zinc, iron, and copper and their role in the immune system. They also look at the fact that vegans, older people, chronically ill, pregnant women, and elite athletes often have nutrient deficiencies that call for supplementation. The agricultural soil in Europe and many other parts of the world is selenium-depleted, which makes it challenging to get enough selenium from our diets. But it is also important not to overdose on minerals. In this article, you can read more about how to optimize your nutrient intake for your immune health. Many people take a multivitamin this time of year. However, even if the manufacturers really squeeze together the ingredients it is impossible to put enough vitamins and minerals in one pill to cover our actual needs. In fact, the manufacturing process determines if we are able to absorb the different nutrients in the first place, and that is important for them to work properly in the body. Therefore, it is vital that you choose a supplement that has good quality, and you must make sure to focus on the vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids that we humans typically tend to lack.
Many people take a multivitamin this time of year. However, even if the manufacturers really squeeze together the ingredients it is impossible to put enough vitamins and minerals in one pill to cover our actual needs. In fact, the manufacturing process determines if we are able to absorb the different nutrients in the first place, and that is important for them to work properly in the body. Therefore, it is vital that you choose a supplement that has good quality, and you must make sure to focus on the vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids that we humans typically tend to lack.

 Nothing beats a good night’s sleep. Still, sleep disturbances are widespread, and surprisingly many people struggle through the day, trying to survive on far too much coffee and other stimulants – and they cannot do anything about the problem. It turns out that many vegetarians, users of birth control pills, older people, and diabetics suffer from sleep problems because they lack
Nothing beats a good night’s sleep. Still, sleep disturbances are widespread, and surprisingly many people struggle through the day, trying to survive on far too much coffee and other stimulants – and they cannot do anything about the problem. It turns out that many vegetarians, users of birth control pills, older people, and diabetics suffer from sleep problems because they lack  Vitamin D’s role in maintaining proper health is well documented. Still, many older people lack the nutrient and that increases their risk of bone fractures, blood poisoning, and disease complications that can eventually lead to hospitalization. Also, they risk prolonged hospitalization according to a new Irish study published in the scientific journal Nutrients. The scientists recommend giving vitamin D supplements to seniors to increase their blood levels of vitamin D. Other studies even suggest that this can protect against COVID-19, as low vitamin D status is associated with an increased risk of being hospitalized with the disease.
Vitamin D’s role in maintaining proper health is well documented. Still, many older people lack the nutrient and that increases their risk of bone fractures, blood poisoning, and disease complications that can eventually lead to hospitalization. Also, they risk prolonged hospitalization according to a new Irish study published in the scientific journal Nutrients. The scientists recommend giving vitamin D supplements to seniors to increase their blood levels of vitamin D. Other studies even suggest that this can protect against COVID-19, as low vitamin D status is associated with an increased risk of being hospitalized with the disease.
 Hashimoto’s disease (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) is an overlooked scourge that leads to hypothyroidism and is particularly widespread among women. Postpartum thyroiditis that also slows down your metabolism follows in the wake of pregnancy. Graves’ disease where the metabolism speeds up (hyperthyroidism) is less common. These three thyroid disorders belong to the group of autoimmune disorders where the immune defense attacks the body’s tissues, and it appears that lack of
Hashimoto’s disease (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) is an overlooked scourge that leads to hypothyroidism and is particularly widespread among women. Postpartum thyroiditis that also slows down your metabolism follows in the wake of pregnancy. Graves’ disease where the metabolism speeds up (hyperthyroidism) is less common. These three thyroid disorders belong to the group of autoimmune disorders where the immune defense attacks the body’s tissues, and it appears that lack of  It is hardly a coincidence that sore throats, colds, flus, and related complications such as sinus infections and pneumonia typically circulate during the winter period. They are primarily a result of having low
It is hardly a coincidence that sore throats, colds, flus, and related complications such as sinus infections and pneumonia typically circulate during the winter period. They are primarily a result of having low  Levels of
Levels of  We need plenty of
We need plenty of 
 Nowadays, fruit, potatoes, and vegetables in general contain very little
Nowadays, fruit, potatoes, and vegetables in general contain very little  More than 25 percent of people older than 65 years have low levels of vitamin D in their blood. Deficiencies in vitamin B12, folic acid, and iron are also common. This is the conclusion of a large study that was conducted by scientists from Helmholtz Zentrum in Munich, Germany. The widespread lack of vitamins and minerals among older people is critical, especially because this population group is increasing. The lack of essential nutrients affects the calcium uptake, immune defense, and nervous system among other things, leaving older people increasingly vulnerable to osteoporosis, influenza, dementia, and a host of other diseases that impair quality of life and burden the entire public health sector.
More than 25 percent of people older than 65 years have low levels of vitamin D in their blood. Deficiencies in vitamin B12, folic acid, and iron are also common. This is the conclusion of a large study that was conducted by scientists from Helmholtz Zentrum in Munich, Germany. The widespread lack of vitamins and minerals among older people is critical, especially because this population group is increasing. The lack of essential nutrients affects the calcium uptake, immune defense, and nervous system among other things, leaving older people increasingly vulnerable to osteoporosis, influenza, dementia, and a host of other diseases that impair quality of life and burden the entire public health sector.
 We need
We need  Older people can easily become deficient of vitamins and minerals, which can weaken their immune system and make them more prone to infections and prolonged periods with disease. On the other hand, older people who take a multivitamin and mineral supplement with zinc and large quantities of vitamin C experience fewer days with disease and have less severe symptoms, according to a placebo-controlled study from Oregon State University. But many multivitamin supplements do not contain enough vitamin D and it is very important for older people to get enough of this nutrient.
Older people can easily become deficient of vitamins and minerals, which can weaken their immune system and make them more prone to infections and prolonged periods with disease. On the other hand, older people who take a multivitamin and mineral supplement with zinc and large quantities of vitamin C experience fewer days with disease and have less severe symptoms, according to a placebo-controlled study from Oregon State University. But many multivitamin supplements do not contain enough vitamin D and it is very important for older people to get enough of this nutrient.
 Periodontal disease affects most people at some stage in life. However, according to a recent study that is published in Contemporary Clinical Dentistry, supplemental use of Q10 and tea tree oil may have potential benefits.
Periodontal disease affects most people at some stage in life. However, according to a recent study that is published in Contemporary Clinical Dentistry, supplemental use of Q10 and tea tree oil may have potential benefits.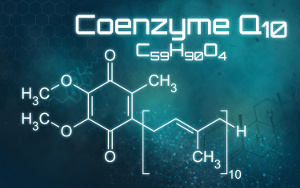 According to WHO, sepsis is the third-most common cause of death, following cardiovascular disease and death. Sepsis is a result of the immune defense overreacting to an infection in the bloodstream. According to a new Slovakian study published in Bratislava Medical Journal, if you start supplementing with
According to WHO, sepsis is the third-most common cause of death, following cardiovascular disease and death. Sepsis is a result of the immune defense overreacting to an infection in the bloodstream. According to a new Slovakian study published in Bratislava Medical Journal, if you start supplementing with  More and more people boost their immune with help from Echinacea, ginger, smoothies, and juices packed with vitamin C, antioxidants and secondary immune-strengthening compounds. Nonetheless, none of these otherwise useful strategies can compensate for the widespread lack of vitamin D that is the underlying reason why so many of us contract virus infections during the winter period.
More and more people boost their immune with help from Echinacea, ginger, smoothies, and juices packed with vitamin C, antioxidants and secondary immune-strengthening compounds. Nonetheless, none of these otherwise useful strategies can compensate for the widespread lack of vitamin D that is the underlying reason why so many of us contract virus infections during the winter period.
 During the winter period, many of us have runny noses and some may end up in bed with a bout of flu. Now is the time to prime your immune system by getting all those vitamins and minerals that your diet is not always able to provide you. That way you can ward off germs and avoid unnecessary sick days. But what effect does
During the winter period, many of us have runny noses and some may end up in bed with a bout of flu. Now is the time to prime your immune system by getting all those vitamins and minerals that your diet is not always able to provide you. That way you can ward off germs and avoid unnecessary sick days. But what effect does  Hormonal imbalances have broad implications and increase the risk of chronic fatigue, overweight, impaired fertility, dry mucosa, hot flushes, slow metabolism, breast cancer, and many other problems. Lack of essential nutrients contributes to such disruptions of the sensitive hormone system. This is also the case with hormone-disrupting compounds.
Hormonal imbalances have broad implications and increase the risk of chronic fatigue, overweight, impaired fertility, dry mucosa, hot flushes, slow metabolism, breast cancer, and many other problems. Lack of essential nutrients contributes to such disruptions of the sensitive hormone system. This is also the case with hormone-disrupting compounds. We are constantly being warned about sun exposure and skin cancer. Still, it is important that we get plenty of
We are constantly being warned about sun exposure and skin cancer. Still, it is important that we get plenty of  During the winter period, many people catch a cold or are bed-ridden with a bout of the flu. They may consider this to be perfectly natural, but it is actually a sign of a weakened immune defense, and that makes them susceptible to contamination. What matters is to make sure to get plenty of vitamin D, vitamin C, selenium, and zinc, all of which are nutrients that have different functions in the immune system. Some nutrients are also needed in larger quantities to tackle a beginning infection, and it is important to act quickly in order to nip the infection in the bud.
During the winter period, many people catch a cold or are bed-ridden with a bout of the flu. They may consider this to be perfectly natural, but it is actually a sign of a weakened immune defense, and that makes them susceptible to contamination. What matters is to make sure to get plenty of vitamin D, vitamin C, selenium, and zinc, all of which are nutrients that have different functions in the immune system. Some nutrients are also needed in larger quantities to tackle a beginning infection, and it is important to act quickly in order to nip the infection in the bud. Undernourishment typically affects the elderly, those with diseases, addicts, and people with eating disorders. The condition increases the risk of serious diseases and repeated hospitalizations and is an enormous economic burden to society. Many undernourished people suffer from loss of appetite, a problem that can often be stimulated with improved diets and supplements of
Undernourishment typically affects the elderly, those with diseases, addicts, and people with eating disorders. The condition increases the risk of serious diseases and repeated hospitalizations and is an enormous economic burden to society. Many undernourished people suffer from loss of appetite, a problem that can often be stimulated with improved diets and supplements of If you are vegetarian or vegan you need keen insight in order to know how to get enough protein, vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, and certain amino acids. Lack of essential nutrients can cause anemia and fatigue but may also increase your risk of serious diseases.
If you are vegetarian or vegan you need keen insight in order to know how to get enough protein, vitamins, minerals, fatty acids, and certain amino acids. Lack of essential nutrients can cause anemia and fatigue but may also increase your risk of serious diseases. It came as good news for vegetarians, vegans and sclerosis sufferers when Danish health authorities allowed strong
It came as good news for vegetarians, vegans and sclerosis sufferers when Danish health authorities allowed strong  Tuberculosis is one of the most common diseases in the world and costs millions of lives, especially in the underdeveloped countries. Tuberculosis typically goes hand in hand with malnutrition, and now a group of scientists from Dublin in Ireland has found that
Tuberculosis is one of the most common diseases in the world and costs millions of lives, especially in the underdeveloped countries. Tuberculosis typically goes hand in hand with malnutrition, and now a group of scientists from Dublin in Ireland has found that  Vitamin B12 is a common term for a group of chemically related substances that all have vitamin activity. They are also known as cobalamins. The biosynthesis of the basic structure is handled by bacteria that are found many places in nature. The uptake of vitamin B12 from food requires the presence of the protein intrinsic factor that is formed in the gastric mucosa. Intrinsic factor binds to vitamin B12 and transports it into the body from the small intestine. Coli bacteria in the colon also produce vitamin B12 that is taken up by the body. Vitamin B12 is stored in the liver for up to several months at a time, and we humans are also able to reuse vitamin B12 that has been absorbed from the intestine. It is generally more difficult for the body to absorb vitamin B12 compared with other vitamins, and our ability to take up the nutrient decreases as we grow older. The synthetic basic form of vitamin B12 is used in nutritional supplements and also as a food additive. The dosages are typically rather large in order to ensure sufficient uptake of the nutrient.
Vitamin B12 is a common term for a group of chemically related substances that all have vitamin activity. They are also known as cobalamins. The biosynthesis of the basic structure is handled by bacteria that are found many places in nature. The uptake of vitamin B12 from food requires the presence of the protein intrinsic factor that is formed in the gastric mucosa. Intrinsic factor binds to vitamin B12 and transports it into the body from the small intestine. Coli bacteria in the colon also produce vitamin B12 that is taken up by the body. Vitamin B12 is stored in the liver for up to several months at a time, and we humans are also able to reuse vitamin B12 that has been absorbed from the intestine. It is generally more difficult for the body to absorb vitamin B12 compared with other vitamins, and our ability to take up the nutrient decreases as we grow older. The synthetic basic form of vitamin B12 is used in nutritional supplements and also as a food additive. The dosages are typically rather large in order to ensure sufficient uptake of the nutrient. Intensive care units in hospitals offer treatment for critically ill patients, who are monitored and receive specialist care around the clock. It goes without saying that this type of medical attention is associated with both suffering and comes with a huge price tag. A whole new meta-analysis has shown that
Intensive care units in hospitals offer treatment for critically ill patients, who are monitored and receive specialist care around the clock. It goes without saying that this type of medical attention is associated with both suffering and comes with a huge price tag. A whole new meta-analysis has shown that  There are several kinds of vitamin D with the two most important being:
There are several kinds of vitamin D with the two most important being: More vitamin D may contribute to better blood sugar regulation in type 2 diabetes. Eggs are a good source of vitamin D, but in the winter period it may be a good idea to take a high-dosed supplement.
More vitamin D may contribute to better blood sugar regulation in type 2 diabetes. Eggs are a good source of vitamin D, but in the winter period it may be a good idea to take a high-dosed supplement.
 According to a study that was presented to a group of endocrinologists at an Edinburgh conference, supplements of
According to a study that was presented to a group of endocrinologists at an Edinburgh conference, supplements of  This time of year, many people suffer from asthma, aching joints, or an exacerbation of other chronic diseases that involve inflammation. This is often because they lack
This time of year, many people suffer from asthma, aching joints, or an exacerbation of other chronic diseases that involve inflammation. This is often because they lack It is hardly a coincidence that so many of us contract virus infections in the course of the winter. It is because we lack
It is hardly a coincidence that so many of us contract virus infections in the course of the winter. It is because we lack  Supplementing with high doses of
Supplementing with high doses of 

 Vitamin D2 occurs naturally in foods from the plant kingdom while vitamin D3 comes from animal sources. It is also vitamin D3 that we synthesize in our skin in response to sun exposure. Scientists from the Universities of Surrey and Brighton in Great Britain have now discovered that the two types of
Vitamin D2 occurs naturally in foods from the plant kingdom while vitamin D3 comes from animal sources. It is also vitamin D3 that we synthesize in our skin in response to sun exposure. Scientists from the Universities of Surrey and Brighton in Great Britain have now discovered that the two types of  Immunotherapy has a special potential when used to treat cancer, which is because this particular type of therapy inhibits special molecules that block the body’s own defense mechanism against cancer cells. A team of scientists from Texas has discovered that
Immunotherapy has a special potential when used to treat cancer, which is because this particular type of therapy inhibits special molecules that block the body’s own defense mechanism against cancer cells. A team of scientists from Texas has discovered that  According to an article that is published in StatPearls,
According to an article that is published in StatPearls,  Large population studies of adults and their diet habits often tend to overlook certain groups such as younger adults. A British study therefore took a closer look at eating habits of adults in their twenties, thirties, forties, and fifties. It revealed a widespread lack of B vitamins, magnesium, potassium, iodine, zinc, and selenium. Being deficient in these essential nutrients can harm your fertility and increase your risk of different diseases, while speeding up concealed ageing processes such as loss of cognition and bone mass.
Large population studies of adults and their diet habits often tend to overlook certain groups such as younger adults. A British study therefore took a closer look at eating habits of adults in their twenties, thirties, forties, and fifties. It revealed a widespread lack of B vitamins, magnesium, potassium, iodine, zinc, and selenium. Being deficient in these essential nutrients can harm your fertility and increase your risk of different diseases, while speeding up concealed ageing processes such as loss of cognition and bone mass.
 It is commonly known that
It is commonly known that 
 An estimated two billion people worldwide lack
An estimated two billion people worldwide lack  Bladder infection is one of the most widespread bacterial infections. It can lead to serious complications such as kidney infections and blood poisoning. A team of scientists from University of Queensland in Australia has discovered new details about
Bladder infection is one of the most widespread bacterial infections. It can lead to serious complications such as kidney infections and blood poisoning. A team of scientists from University of Queensland in Australia has discovered new details about  The mineral
The mineral Even minor
Even minor 
 "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.