| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (18.13KB) (27.63%) | 46.41ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (4.66KB) (20.59%) | 34.58ms |
| 1 x afterRenderComponent com_tags (1.93MB) (19.43%) | 32.63ms |
| 1 x afterInitialise (1.28MB) (10.95%) | 18.38ms |
| 1 x afterLoad (456.41KB) (2.78%) | 4.67ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (423.86KB) (2.76%) | 4.63ms |
| 1 x afterRender (327.41KB) (2.67%) | 4.48ms |
| 1 x afterRoute (840.02KB) (2.64%) | 4.43ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (1.31%) | 2.19ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (0.97%) | 1.64ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (22.56KB) (0.87%) | 1.46ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (192.45KB) (0.82%) | 1.38ms |
| 1 x afterDispatch (27.48KB) (0.81%) | 1.35ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.66KB) (0.48%) | 812μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (0.45%) | 753μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (25.14KB) (0.4%) | 676μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (0.38%) | 632μs |
| 1 x After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (0.34%) | 578μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (21.04KB) (0.3%) | 512μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (0.29%) | 491μs |
| 1 x Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (0.28%) | 467μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (0.19%) | 326μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.75KB) (0.19%) | 313μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (0.18%) | 295μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (0.14%) | 230μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (0.11%) | 192μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (0.11%) | 179μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (0.09%) | 157μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (0.08%) | 133μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (0.06%) | 105μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (0.06%) | 95μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (0.05%) | 83μs |
| 1 x After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (0.03%) | 55μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (0.03%) | 55μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (0.03%) | 55μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (0.03%) | 48μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (0.03%) | 47μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (0.03%) | 45μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (0.03%) | 43μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (0.03%) | 43μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (0.02%) | 40μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (0.02%) | 39μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (0.02%) | 33μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (0.02%) | 33μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (0.02%) | 31μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (0.02%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (0.02%) | 28μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (0.01%) | 25μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (0.01%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (0.01%) | 24μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (0.01%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (0.01%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (0.01%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (0.01%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (0.01%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (0.01%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (0.01%) | 17μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (0.01%) | 16μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (0.01%) | 16μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (0.01%) | 16μs |
| 1 x Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (0.01%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (0.01%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (0.01%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (0.01%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (0.01%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (0.01%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (0.01%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (0.01%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (0.01%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (0.01%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (0.01%) | 11μs |
| 3 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (0.01%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (0.01%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (0.01%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (0.01%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (0.01%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (0.01%) | 10μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (0.01%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (0.01%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (0%) | 5μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (0%) | 4μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (0%) | 3μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (0%) | 2μs |
 Lack of dietary vitamin A increases the risk of skin infections and acne. Science has known for a long time that creams with synthetic vitamin A can be used against various skin problems, yet they do not know how vitamin A really works. Now, a study conducted by scientists from UT Southwestern Medical Center in Texas, USA, reveals the underlying mechanisms by identifying a bactericidal skin protein that requires vitamin A in order to work. But what kind of vitamin is vitamin A really? When does it work optimally? And is there in fact vitamin A in carrots?
Lack of dietary vitamin A increases the risk of skin infections and acne. Science has known for a long time that creams with synthetic vitamin A can be used against various skin problems, yet they do not know how vitamin A really works. Now, a study conducted by scientists from UT Southwestern Medical Center in Texas, USA, reveals the underlying mechanisms by identifying a bactericidal skin protein that requires vitamin A in order to work. But what kind of vitamin is vitamin A really? When does it work optimally? And is there in fact vitamin A in carrots?







 We all know the importance of eating a healthy diet, exercising, getting sufficient sleep, and sunbathing with caution. Still, life is not always that simple, and even if we stick with the official guidelines for healthy living, it can often be challenging to get adequate amounts of the essential nutrients. Nonetheless, supplements are useful as compensation for these shortcomings. In fact, the use of such products can be compared with plant fertilizers that make plants look healthy, flourish and thrive
We all know the importance of eating a healthy diet, exercising, getting sufficient sleep, and sunbathing with caution. Still, life is not always that simple, and even if we stick with the official guidelines for healthy living, it can often be challenging to get adequate amounts of the essential nutrients. Nonetheless, supplements are useful as compensation for these shortcomings. In fact, the use of such products can be compared with plant fertilizers that make plants look healthy, flourish and thrive Poor wound healing, a somewhat common and well-known problem, especially among hospital patients, is associated with huge health costs. Proper wound healing is contingent upon on the presence of different nutrients, and it appears that the ratio between
Poor wound healing, a somewhat common and well-known problem, especially among hospital patients, is associated with huge health costs. Proper wound healing is contingent upon on the presence of different nutrients, and it appears that the ratio between  According to a new study that is published in the British Journal of Nutrition, even minor
According to a new study that is published in the British Journal of Nutrition, even minor  Having healthy-looking hair means a lot to most people. Hair that splits at the ends, hair loss, and other hair problems may be caused by stress, hormone changes, and numerous other factors. In this article, we will take a closer look at the diet and its impact on hair health, and we will look at available studies of protein, iron, zinc, selenium, silica, B vitamins, vitamin D and vitamin A. The fact is, we need plenty of these nutrients in a form that the body can absorb and utilize. On the other hand, getting too much can do more harm than good, according to an article in Dermatology Practical & Conceptual, in which the author has analyzed the available research.
Having healthy-looking hair means a lot to most people. Hair that splits at the ends, hair loss, and other hair problems may be caused by stress, hormone changes, and numerous other factors. In this article, we will take a closer look at the diet and its impact on hair health, and we will look at available studies of protein, iron, zinc, selenium, silica, B vitamins, vitamin D and vitamin A. The fact is, we need plenty of these nutrients in a form that the body can absorb and utilize. On the other hand, getting too much can do more harm than good, according to an article in Dermatology Practical & Conceptual, in which the author has analyzed the available research. Those with a higher dietary intake of
Those with a higher dietary intake of  “Before, I was losing hair but it stopped when I started taking selenium. Even my nails seem to be a lot stronger now,” says Maria Remenyi, a 70-year old lady who is amazed with the effect of the selenium tablets with zinc that she is taking.
“Before, I was losing hair but it stopped when I started taking selenium. Even my nails seem to be a lot stronger now,” says Maria Remenyi, a 70-year old lady who is amazed with the effect of the selenium tablets with zinc that she is taking. New Year’s resolutions are often related to healthier living with better dietary choices, fewer stimulants, and more exercise. We want to stay as young and vital as possible with lots of energy. However, life is not always that simple, and nature often needs a helping hand. The following anti-ageing tips – including the essential beauty sleep – are based on a summary of articles that have all been published previously on this site.
New Year’s resolutions are often related to healthier living with better dietary choices, fewer stimulants, and more exercise. We want to stay as young and vital as possible with lots of energy. However, life is not always that simple, and nature often needs a helping hand. The following anti-ageing tips – including the essential beauty sleep – are based on a summary of articles that have all been published previously on this site. You probably spend a fortune already on expensive face creams and the like but did you know that a supplement combining two specific micronutrients is one of the best things you can take for your skin, hair, and nails? More and more women include selenium and zinc as part of their daily routine for beauty and appearance and find that it works surprisingly well.
You probably spend a fortune already on expensive face creams and the like but did you know that a supplement combining two specific micronutrients is one of the best things you can take for your skin, hair, and nails? More and more women include selenium and zinc as part of their daily routine for beauty and appearance and find that it works surprisingly well.
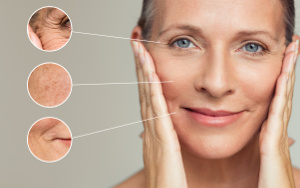
 The condition of our skin means a lot to our appearance and health, and being deficient in one or several nutrients can cause premature skin ageing. Also, things like poor wound healing, acne, herpes infections, yeast infections, eczema, psoriasis, and other skin disorders may occur. In a review article published in Medicina, scientists have looked at the role of vitamins A, C, E, D, and biotin plus omega-3 fatty acids in skin health. Studies suggest that selenium and zinc may also be important for healthy skin and anti-ageing. If you don’t get enough of these nutrients or if you simply have an increased need for them, you may consider taking a supplement.
The condition of our skin means a lot to our appearance and health, and being deficient in one or several nutrients can cause premature skin ageing. Also, things like poor wound healing, acne, herpes infections, yeast infections, eczema, psoriasis, and other skin disorders may occur. In a review article published in Medicina, scientists have looked at the role of vitamins A, C, E, D, and biotin plus omega-3 fatty acids in skin health. Studies suggest that selenium and zinc may also be important for healthy skin and anti-ageing. If you don’t get enough of these nutrients or if you simply have an increased need for them, you may consider taking a supplement. An important element in skincare and natural anti-ageing is to protect our cells against free radicals, which are aggressive oxygen compounds that we humans are exposed to. The free radical burden increases tremendously as a result of stress, too little sleep, ageing processes, smoking, inflammation, poisoning, medical drugs, and sunburns. Our only source of protection against free radicals is the presence of different antioxidants such as vitamins A, C, and E, selenium, zinc, and Q10, but we also need essential fatty acids. Optimal skincare requires that we get adequate quantities of the different nutrients, which are also an important element in our energy turnover. But what is skin ageing really? And why can we not simply stop it with anti-wrinkle creams, Botox, and plastic surgery? Also, which antioxidants and essential fatty acids are difficult to get in the right quantities?
An important element in skincare and natural anti-ageing is to protect our cells against free radicals, which are aggressive oxygen compounds that we humans are exposed to. The free radical burden increases tremendously as a result of stress, too little sleep, ageing processes, smoking, inflammation, poisoning, medical drugs, and sunburns. Our only source of protection against free radicals is the presence of different antioxidants such as vitamins A, C, and E, selenium, zinc, and Q10, but we also need essential fatty acids. Optimal skincare requires that we get adequate quantities of the different nutrients, which are also an important element in our energy turnover. But what is skin ageing really? And why can we not simply stop it with anti-wrinkle creams, Botox, and plastic surgery? Also, which antioxidants and essential fatty acids are difficult to get in the right quantities? Sulphur is essential for plants and animals. An adult contains around 175 grams of sulphur. The nutrient is found in the amino acids cysteine and methionine and is therefore also present in all the proteins and enzymes that contain these amino acids. Sulphur is a component of those enzymes that are responsible for ensuring that the hemoglobin in red blood cells is able to bind oxygen. Sulphur is also a component of the disulfide bonds that give strength to skin, hair, and nails. The reason why bird eggs have such a high sulphur content is that the nutrient is needed for the plumage of the developing bird. Sulphur is able to bind heavy metals and other toxins. Sulphur is chemically similar to selenium, but sulphur is not an antioxidant and has other functions in the body.
Sulphur is essential for plants and animals. An adult contains around 175 grams of sulphur. The nutrient is found in the amino acids cysteine and methionine and is therefore also present in all the proteins and enzymes that contain these amino acids. Sulphur is a component of those enzymes that are responsible for ensuring that the hemoglobin in red blood cells is able to bind oxygen. Sulphur is also a component of the disulfide bonds that give strength to skin, hair, and nails. The reason why bird eggs have such a high sulphur content is that the nutrient is needed for the plumage of the developing bird. Sulphur is able to bind heavy metals and other toxins. Sulphur is chemically similar to selenium, but sulphur is not an antioxidant and has other functions in the body.
 Vitamin B2 is water-soluble and because it does not get stored in the body we depend on regular intake of the nutrient. Vitamin B2 is also known as lactoflavin and is used as a yellow colouring agent/additive in various foods. When ingested in very large quantities vitamin B2 causes the urine to turn highly yellow. Vitamin B2 is destroyed by light, heating, and alcohol.
Vitamin B2 is water-soluble and because it does not get stored in the body we depend on regular intake of the nutrient. Vitamin B2 is also known as lactoflavin and is used as a yellow colouring agent/additive in various foods. When ingested in very large quantities vitamin B2 causes the urine to turn highly yellow. Vitamin B2 is destroyed by light, heating, and alcohol. Photodynamic therapy is a kind of light therapy that is used to treat skin cancer, psoriasis, and other skin diseases. According to a review article published in Nutrients,
Photodynamic therapy is a kind of light therapy that is used to treat skin cancer, psoriasis, and other skin diseases. According to a review article published in Nutrients,  An estimated two billion people worldwide lack
An estimated two billion people worldwide lack  Even minor
Even minor 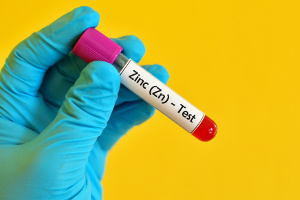
 Our skin is among the body’s organs that contains the most zinc, and the trace element is of vital importance to the formation and protection of skin cells. A zinc deficiency can therefore contribute to poor wound healing, sensitive skin, acne, eczema and other skin disorders, and hair loss, according to a new study that is published in the scientific journal Nutrients. Although clinical zinc deficiencies are rare in our part of the world, sub-clinical deficiencies are rather common. For instance, vegetarians, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and older people are particularly vulnerable. A large intake of sugar, calcium, and alcohol, the use of birth control pills and several types of medicine, plus certain diseases and other factors can also increase your risk of becoming zinc-deficient.
Our skin is among the body’s organs that contains the most zinc, and the trace element is of vital importance to the formation and protection of skin cells. A zinc deficiency can therefore contribute to poor wound healing, sensitive skin, acne, eczema and other skin disorders, and hair loss, according to a new study that is published in the scientific journal Nutrients. Although clinical zinc deficiencies are rare in our part of the world, sub-clinical deficiencies are rather common. For instance, vegetarians, pregnant and breastfeeding women, and older people are particularly vulnerable. A large intake of sugar, calcium, and alcohol, the use of birth control pills and several types of medicine, plus certain diseases and other factors can also increase your risk of becoming zinc-deficient. "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.