afterLoad (456.22KB) (1.98ms)
afterInitialise (1.27MB) (28.55ms)
afterRoute (840.48KB) (12.62ms)
beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.62KB) (227μs)
afterRenderComponent com_tags (3.98MB) (205ms)
afterDispatch (27.47KB) (2.6ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (423.86KB) (11.9ms)
Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (1.77ms)
After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (127.55KB) (615μs)
Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (15μs)
After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (43μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (7.93KB) (126ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (28μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (1.3ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (19μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (44.91KB) (105ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (30μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (79μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (13μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (26μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (10μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (20μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (19μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (17μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (8μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (19μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (12μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (491μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (18μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (285μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (16μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (281μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (13μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (31μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (2.04ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (42μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (4μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (64μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (13μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (23μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (30μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (325μs)
afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (41μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (12μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (26μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (11μs)
afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (33μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (11μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (24μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (23μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (25.14KB) (707μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (186.95KB) (1.35ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (4μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (62μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (17μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (22.55KB) (1.6ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (10μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (1.62ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (32μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (142μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.66KB) (852μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (51μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (103μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (760μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (47μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (18μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (765μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (37μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (574μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (46μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (183μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (133μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (25μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (84μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (92μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (21μs)
afterRender (818.8KB) (11.15ms)
| 1 x afterRenderComponent com_tags (3.98MB) (39.25%) | 205.48ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (7.93KB) (24.09%) | 126.09ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (44.91KB) (20.01%) | 104.73ms |
| 1 x afterInitialise (1.27MB) (5.45%) | 28.55ms |
| 1 x afterRoute (840.48KB) (2.41%) | 12.62ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (423.86KB) (2.27%) | 11.90ms |
| 1 x afterRender (818.8KB) (2.13%) | 11.15ms |
| 1 x afterDispatch (27.47KB) (0.5%) | 2.60ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (0.39%) | 2.04ms |
| 1 x afterLoad (456.22KB) (0.38%) | 1.98ms |
| 1 x Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (0.34%) | 1.77ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (0.31%) | 1.62ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (22.55KB) (0.3%) | 1.60ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (186.95KB) (0.26%) | 1.35ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (0.25%) | 1.30ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.66KB) (0.16%) | 852μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (0.15%) | 765μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (0.15%) | 760μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (25.14KB) (0.14%) | 707μs |
| 1 x After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (127.55KB) (0.12%) | 615μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (0.11%) | 574μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (0.09%) | 491μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (0.06%) | 325μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (0.05%) | 285μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (0.05%) | 281μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.62KB) (0.04%) | 227μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (0.03%) | 183μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (0.03%) | 142μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (0.03%) | 133μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (0.02%) | 103μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (0.02%) | 92μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (0.02%) | 84μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (0.02%) | 79μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 64μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (0.01%) | 62μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (0.01%) | 51μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 47μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (0.01%) | 46μs |
| 1 x After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (0.01%) | 43μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (0.01%) | 42μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 41μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 37μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 33μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (0.01%) | 32μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (0.01%) | 31μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (0.01%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 30μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (0.01%) | 28μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (0%) | 26μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (0%) | 26μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (0%) | 25μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (0%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (0%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (0%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (0%) | 20μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (0%) | 17μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (0%) | 17μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (0%) | 16μs |
| 1 x Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (0%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (0%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (0%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (0%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (0%) | 10μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 3 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (0%) | 6μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (0%) | 5μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (0%) | 4μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (0%) | 2μs |
 According to the statistics, far too many patients contract an infection while being hospitalized in a Danish hospital. This has enormous human and economic costs that need to be addressed. Hospital infections are not only a consequence of poor hygiene, it actually turns out that 40 percent of the patients are malnourished to some degree, which impairs their immune system and makes them an easier target for infections. Lack of vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium, zinc, and iron seem to be the big and overlooked problem.
According to the statistics, far too many patients contract an infection while being hospitalized in a Danish hospital. This has enormous human and economic costs that need to be addressed. Hospital infections are not only a consequence of poor hygiene, it actually turns out that 40 percent of the patients are malnourished to some degree, which impairs their immune system and makes them an easier target for infections. Lack of vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium, zinc, and iron seem to be the big and overlooked problem.







 A lot of sports and fitness disciplines are indoor activities. According to a new American study, this increases the risk of becoming vitamin D-deficient. Not only can a
A lot of sports and fitness disciplines are indoor activities. According to a new American study, this increases the risk of becoming vitamin D-deficient. Not only can a  If you have a large waist circumference, you are more likely to have low blood levels of
If you have a large waist circumference, you are more likely to have low blood levels of  It is not the actual COVID-19 virus that can become lethal. It is the immune system’s overreaction with hyperinflammation and a storm of cytokines that destroys healthy tissue in the lungs, the cardiovascular system, and other places in the body, according to a new article that is published in The Lancet. The capacity of the immune system determines if an infection like COVID-19 is either harmless or life-threatening. For that reason, hygienic measures, masks, isolation, and delayed vaccines are not sufficient. We also need to bolster our immune system against COVID-19 and other pandemics that may occur in the future. Let’s look closer at vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium and zinc, all of which are essential for preventing a well-functioning immune system from going off its rails. What is also worth mentioning is that many people lack these nutrients, especially older people and other exposed groups.
It is not the actual COVID-19 virus that can become lethal. It is the immune system’s overreaction with hyperinflammation and a storm of cytokines that destroys healthy tissue in the lungs, the cardiovascular system, and other places in the body, according to a new article that is published in The Lancet. The capacity of the immune system determines if an infection like COVID-19 is either harmless or life-threatening. For that reason, hygienic measures, masks, isolation, and delayed vaccines are not sufficient. We also need to bolster our immune system against COVID-19 and other pandemics that may occur in the future. Let’s look closer at vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium and zinc, all of which are essential for preventing a well-functioning immune system from going off its rails. What is also worth mentioning is that many people lack these nutrients, especially older people and other exposed groups. It is no coincidence that sclerosis is more prevalent at the northern latitudes. A major factor is lack of
It is no coincidence that sclerosis is more prevalent at the northern latitudes. A major factor is lack of  Taking a supplement of
Taking a supplement of According to a new study from Johns Hopkins University in the United States,
According to a new study from Johns Hopkins University in the United States, 

 It has been known for a long time that a lack of
It has been known for a long time that a lack of  A new British study that is published in British Journal of Nutrition shows that getting too little
A new British study that is published in British Journal of Nutrition shows that getting too little  According to Bruce Ames, an American biochemist, ageing processes are largely due to lack of nutrients. One important contributing factor is the fact that our uptake and utilization of vitamins and minerals decrease with age. In addition, a lot of different types of medicine block our ability to utilize different nutrients. As a result of this, many of our enzyme processes slow down, making our cells increasingly vulnerable and that increases our risk of disease. Nonetheless, there is a lot we can do to optimize our intake and utilization of nutrients, particularly with respect to vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, iron, selenium, and zinc. It is also worth taking a look at Q10 for energy turnover and melatonin for healthy sleep. Our endogenous synthesis of both compounds decreases with age.
According to Bruce Ames, an American biochemist, ageing processes are largely due to lack of nutrients. One important contributing factor is the fact that our uptake and utilization of vitamins and minerals decrease with age. In addition, a lot of different types of medicine block our ability to utilize different nutrients. As a result of this, many of our enzyme processes slow down, making our cells increasingly vulnerable and that increases our risk of disease. Nonetheless, there is a lot we can do to optimize our intake and utilization of nutrients, particularly with respect to vitamin B12, vitamin D, calcium, iron, selenium, and zinc. It is also worth taking a look at Q10 for energy turnover and melatonin for healthy sleep. Our endogenous synthesis of both compounds decreases with age.
 A cold beer with lunch or a glass of red wine to go with your steak may be tempting. In fact, alcohol in limited amounts can be relaxing and it provides beneficial antioxidants. However, Danes drink too much, and our excessive alcohol consumption is one of the worst threats to public health. Many alcoholics suffer from unstable blood sugar levels, which can have a rather bad impact on their willpower. In addition, the empty calories deplete the body’s levels of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids, on which the nervous system, the brain, and the liver depend. This can easily turn into a vicious cycle. Therefore, having stable blood sugar and making sure to get plenty of vital nutrients is important for preventing and treating alcohol abuse.
A cold beer with lunch or a glass of red wine to go with your steak may be tempting. In fact, alcohol in limited amounts can be relaxing and it provides beneficial antioxidants. However, Danes drink too much, and our excessive alcohol consumption is one of the worst threats to public health. Many alcoholics suffer from unstable blood sugar levels, which can have a rather bad impact on their willpower. In addition, the empty calories deplete the body’s levels of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids, on which the nervous system, the brain, and the liver depend. This can easily turn into a vicious cycle. Therefore, having stable blood sugar and making sure to get plenty of vital nutrients is important for preventing and treating alcohol abuse. Although the development of Alzheimer’s disease is complex, evidence suggests that vitamin deficiencies play a significant and often overlooked role. This is especially true for vitamin C, which supports neuronal health in multiple ways. Deficiencies in
Although the development of Alzheimer’s disease is complex, evidence suggests that vitamin deficiencies play a significant and often overlooked role. This is especially true for vitamin C, which supports neuronal health in multiple ways. Deficiencies in  Veganism is on the rise, and experts have different views on whether or not plant-diets are suited for children. A team of Polish scientists has now discovered that children on vegan diets have low stature and lower bone density than children who eat meat and dairy products. Children on vegan diets also are also more likely to lack amino acids,
Veganism is on the rise, and experts have different views on whether or not plant-diets are suited for children. A team of Polish scientists has now discovered that children on vegan diets have low stature and lower bone density than children who eat meat and dairy products. Children on vegan diets also are also more likely to lack amino acids,  Lack of
Lack of 
 We all need loads of energy to help us through the day feeling on top of the world. Needless to say, this requires stable blood sugar levels, daylight, exercise, and a good night’s sleep. But what are the energy-providing substances in our food? And why are Q10 and particular vitamins and minerals so essential for our energy metabolism and our physical and mental well-being? An article recently published in Medical News Today looks at this and explains that being deficient of a single nutrient can affect our metabolism, energy levels, and weight regulation. Luckily, this can be compensated for so we get the necessary energy boost.
We all need loads of energy to help us through the day feeling on top of the world. Needless to say, this requires stable blood sugar levels, daylight, exercise, and a good night’s sleep. But what are the energy-providing substances in our food? And why are Q10 and particular vitamins and minerals so essential for our energy metabolism and our physical and mental well-being? An article recently published in Medical News Today looks at this and explains that being deficient of a single nutrient can affect our metabolism, energy levels, and weight regulation. Luckily, this can be compensated for so we get the necessary energy boost.
 Melanoma is a type of malignant skin cancer that spreads rapidly. Being vitamin D-deficient doubles the risk of dying of the disease, according to a Spanish study that was presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology congress. It is commonly known that sunburns, which one should generally avoid, increase the risk of contracting skin cancer. But we must not forget that the summer sun is our main source of
Melanoma is a type of malignant skin cancer that spreads rapidly. Being vitamin D-deficient doubles the risk of dying of the disease, according to a Spanish study that was presented at the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology congress. It is commonly known that sunburns, which one should generally avoid, increase the risk of contracting skin cancer. But we must not forget that the summer sun is our main source of  According to Danish research, more than one in three women suspect that their birth control pills cause side effects. Other studies show that birth control pills affect the body’s ability to utilize several different B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin E, magnesium, selenium, and zinc. The lack of these essential nutrients contributes to a number of common side effects such as fluid retention, blood clots, cancer, and depression.
According to Danish research, more than one in three women suspect that their birth control pills cause side effects. Other studies show that birth control pills affect the body’s ability to utilize several different B vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin E, magnesium, selenium, and zinc. The lack of these essential nutrients contributes to a number of common side effects such as fluid retention, blood clots, cancer, and depression. Blood levels of
Blood levels of  Type 2 diabetes is spreading like a bushfire. An alarmingly many people have metabolic syndrome – or pre-diabetes – which is characterized by insulin resistance, hypertension, elevated cholesterol levels and abdominal obesity (apple-shaped body). Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome are associated with enormous human and socio-economic costs. In this article, we will look closer at chromium, vitamin D, magnesium, and coenzyme Q10 plus relevant diet changes to see how they can positively affect blood sugar levels, cholesterol balance, and weight control. We will also take a closer look at supplements that are able to prevent diabetic neuropathy, a disorder that can lead to amputations.
Type 2 diabetes is spreading like a bushfire. An alarmingly many people have metabolic syndrome – or pre-diabetes – which is characterized by insulin resistance, hypertension, elevated cholesterol levels and abdominal obesity (apple-shaped body). Type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome are associated with enormous human and socio-economic costs. In this article, we will look closer at chromium, vitamin D, magnesium, and coenzyme Q10 plus relevant diet changes to see how they can positively affect blood sugar levels, cholesterol balance, and weight control. We will also take a closer look at supplements that are able to prevent diabetic neuropathy, a disorder that can lead to amputations. Breast cancer is very common in the Western world and modern society. The disease is thought to be associated with lifestyle factors and lack of essential nutrients. For instance, it has been known for a long time that lack of vitamin D increases the risk of breast cancer. According to a new study that is published in the science journal Endocrinology, there is also a link between lack of vitamin D and the development of metastases in the lungs. Previous research also shows that the widespread deficiency of selenium, iodine, omega-3 fatty acids, and melatonin can increase the risk of breast cancer but supplements can help prevent the disease and possibly be used as add-on therapy.
Breast cancer is very common in the Western world and modern society. The disease is thought to be associated with lifestyle factors and lack of essential nutrients. For instance, it has been known for a long time that lack of vitamin D increases the risk of breast cancer. According to a new study that is published in the science journal Endocrinology, there is also a link between lack of vitamin D and the development of metastases in the lungs. Previous research also shows that the widespread deficiency of selenium, iodine, omega-3 fatty acids, and melatonin can increase the risk of breast cancer but supplements can help prevent the disease and possibly be used as add-on therapy. Allergic diseases such as asthma, hay fever, food allergies and contact dermatitis are becoming increasingly common. It makes a big difference to breastfeed for at least six months because breast milk contains various compounds that strengthen the child’s gut flora and immune defense.
Allergic diseases such as asthma, hay fever, food allergies and contact dermatitis are becoming increasingly common. It makes a big difference to breastfeed for at least six months because breast milk contains various compounds that strengthen the child’s gut flora and immune defense.  COVID-19 represents a serious global threat against public health and the economy because we still lack a vaccine and effective therapies. When COVID-19 becomes life-threatening it is primarily because the immune defense overreacts with a cytokine storm and hyperinflammation that destroys healthy tissue in the lungs, the circulatory system, and other places. Older people and heart failure patients already suffer from chronic low-grade, uncontrolled inflammation, to which nutrient deficiencies contribute and make the patients increasingly vulnerable. This also applies to people with metabolic syndrome and diabetes, many of which are overweight. For that reason, scientists affiliated with universities and research centers in Norway, Sweden, and Russia have searched the scientific literature to find studies that focus on whether supplementation with vitamin D, selenium, and zinc can help prevent a COVID-19 infection from escalating and becoming life-threatening.
COVID-19 represents a serious global threat against public health and the economy because we still lack a vaccine and effective therapies. When COVID-19 becomes life-threatening it is primarily because the immune defense overreacts with a cytokine storm and hyperinflammation that destroys healthy tissue in the lungs, the circulatory system, and other places. Older people and heart failure patients already suffer from chronic low-grade, uncontrolled inflammation, to which nutrient deficiencies contribute and make the patients increasingly vulnerable. This also applies to people with metabolic syndrome and diabetes, many of which are overweight. For that reason, scientists affiliated with universities and research centers in Norway, Sweden, and Russia have searched the scientific literature to find studies that focus on whether supplementation with vitamin D, selenium, and zinc can help prevent a COVID-19 infection from escalating and becoming life-threatening.

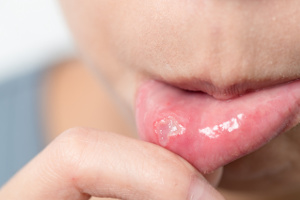 Around 25 percent of adults have had canker sores, also referred to as recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). The condition is characterized by painful, superficial sores, and we don’t know all that much about what causes it or how to treat it. However, according to a meta-analysis that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, a possible cause may be low blood levels of
Around 25 percent of adults have had canker sores, also referred to as recurrent aphthous stomatitis (RAS). The condition is characterized by painful, superficial sores, and we don’t know all that much about what causes it or how to treat it. However, according to a meta-analysis that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, a possible cause may be low blood levels of  A growing number of children are affected by asthma, which is associated with a reduced quality of life. Diet plays a significant role in the development of the disease, and it appears that excessive sugar intake from breakfast cereals, soft drinks, candy, and other sources increases the risk. A deficiency in
A growing number of children are affected by asthma, which is associated with a reduced quality of life. Diet plays a significant role in the development of the disease, and it appears that excessive sugar intake from breakfast cereals, soft drinks, candy, and other sources increases the risk. A deficiency in  Children and youngsters who are exposed to lots of sunlight and have plenty of
Children and youngsters who are exposed to lots of sunlight and have plenty of 



 According to a new study based on a number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, the widespread lack of
According to a new study based on a number of systematic reviews and meta-analyses, the widespread lack of 
 The coronavirus has spread from Wuhan in China to a number of continents, where it has caused massive fear and affected daily life and the global economy. Although most people that get the infection experience a mild course of events, the greatest fear is the potentially life-threatening complications in the respiratory system caused by oxidative stress, which have already taken thousands of human lives. Chinese scientists now call for early intravenous therapy with large doses of vitamin C to prevent oxidative stress and the life-threatening complications that follow in the wake of a derailed immune system. Many researchers also claim that higher intake of vitamin C from dietary sources or supplements help prevent by boosting and regulating the immune system in the upper respiratory tract. The same goes for vitamin D and selenium.
The coronavirus has spread from Wuhan in China to a number of continents, where it has caused massive fear and affected daily life and the global economy. Although most people that get the infection experience a mild course of events, the greatest fear is the potentially life-threatening complications in the respiratory system caused by oxidative stress, which have already taken thousands of human lives. Chinese scientists now call for early intravenous therapy with large doses of vitamin C to prevent oxidative stress and the life-threatening complications that follow in the wake of a derailed immune system. Many researchers also claim that higher intake of vitamin C from dietary sources or supplements help prevent by boosting and regulating the immune system in the upper respiratory tract. The same goes for vitamin D and selenium. When it comes to battling COVID-19, the main focus is on hygiene, face masks, lockdown, and delayed vaccines. For several months, scientists have urged people to take
When it comes to battling COVID-19, the main focus is on hygiene, face masks, lockdown, and delayed vaccines. For several months, scientists have urged people to take  COVID-19 is highly unpredictable and be either totally harmless or life-threatening. Scientists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee recently made a comprehensive genetic analysis that reveals a new hypothesis – the bradykinin hypothesis – which shows why COVID-19 attacks the way it does, why symptoms vary, and why some groups of people are more vulnerable than others. The hypothesis also underpins the importance of getting enough
COVID-19 is highly unpredictable and be either totally harmless or life-threatening. Scientists from Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee recently made a comprehensive genetic analysis that reveals a new hypothesis – the bradykinin hypothesis – which shows why COVID-19 attacks the way it does, why symptoms vary, and why some groups of people are more vulnerable than others. The hypothesis also underpins the importance of getting enough  It has already been documented that the widespread problems with vitamin D deficiency increase the risk of being infected with COVID-19 and developing life-threatening complications. In a new study, a team of Turkish scientists has demonstrated that swift treatment with
It has already been documented that the widespread problems with vitamin D deficiency increase the risk of being infected with COVID-19 and developing life-threatening complications. In a new study, a team of Turkish scientists has demonstrated that swift treatment with  Since December of 2021, two large meta-analyses have revealed that having low levels of
Since December of 2021, two large meta-analyses have revealed that having low levels of  Several studies have shown that optimizing your blood
Several studies have shown that optimizing your blood 
 According to a retrospective study of older COVID-19 patients, lack of
According to a retrospective study of older COVID-19 patients, lack of  Many people avoid dairy products because they are lactose intolerant, are vegan, or for other reasons. Milk is a good source of nutrients, especially calcium, but you can easily get enough calcium from other food sources. What is more, it appears that vitamin D, vitamin K2, and the calcium/magnesium ratio is even more important than calcium alone for the structure and maintenance of strong bones. Another thing to remember is that sugar, soft drinks, stimulants, and certain types of medicine can disrupt the bone-building processes. Therefore, having strong bones is about a lot more than dairy products and calcium alone. Finally, don’t forget that daily weight-bearing exercise stimulates bone density.
Many people avoid dairy products because they are lactose intolerant, are vegan, or for other reasons. Milk is a good source of nutrients, especially calcium, but you can easily get enough calcium from other food sources. What is more, it appears that vitamin D, vitamin K2, and the calcium/magnesium ratio is even more important than calcium alone for the structure and maintenance of strong bones. Another thing to remember is that sugar, soft drinks, stimulants, and certain types of medicine can disrupt the bone-building processes. Therefore, having strong bones is about a lot more than dairy products and calcium alone. Finally, don’t forget that daily weight-bearing exercise stimulates bone density. The summer sun is our most important source of
The summer sun is our most important source of 
 There is a link between depression, dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Also, it appears that chronic stress contributes to oxidative stress and brain cell damage. In a review article that is published in the science journal Antioxidants, researchers look closer at how oxidative stress affects the brain. They also study how antioxidants can be included in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, and why the most promising results are seen with selenium, Q10, melatonin, vitamin E, turmeric, and polyphenols. With regard to depression, selenium, zinc, vitamin E, turmeric, and saffron have demonstrated the greatest potential.
There is a link between depression, dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Also, it appears that chronic stress contributes to oxidative stress and brain cell damage. In a review article that is published in the science journal Antioxidants, researchers look closer at how oxidative stress affects the brain. They also study how antioxidants can be included in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, and why the most promising results are seen with selenium, Q10, melatonin, vitamin E, turmeric, and polyphenols. With regard to depression, selenium, zinc, vitamin E, turmeric, and saffron have demonstrated the greatest potential. Most people with type 2 diabetes have hidden deficiencies in nutrients such as
Most people with type 2 diabetes have hidden deficiencies in nutrients such as  Diabetes is spreading like a bushfire across the globe, but even if governments, doctors, and health authorities have tried desperately to bend the curve, they have not succeeded so far. On the contrary. Today, diabetes is controlled with help from different medical drugs that do not address the underlying cause and actually affect or organ systems. Because of this, diabetics often have impaired quality of life and shorter lifespans than healthy individuals. What is more, diabetics have widespread vitamin B12 and vitamin D deficiencies, which are associated with diabetic neuropathy, which is a serious complication. Cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) are also linked to reduced levels of Q10, a compound that is necessary for energy turnover, the heart, and the cardiovascular system.
Diabetes is spreading like a bushfire across the globe, but even if governments, doctors, and health authorities have tried desperately to bend the curve, they have not succeeded so far. On the contrary. Today, diabetes is controlled with help from different medical drugs that do not address the underlying cause and actually affect or organ systems. Because of this, diabetics often have impaired quality of life and shorter lifespans than healthy individuals. What is more, diabetics have widespread vitamin B12 and vitamin D deficiencies, which are associated with diabetic neuropathy, which is a serious complication. Cholesterol-lowering drugs (statins) are also linked to reduced levels of Q10, a compound that is necessary for energy turnover, the heart, and the cardiovascular system. A panel of physicians and professors collaborating with the Swiss Society for Nutrition (SSN) recently reviewed the scientific evidence on the role of micronutrients in supporting a well-functioning immune defense for optimal health with particular focus on viral infections related to COVID-19. They conclude that there is widespread lack of vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, all of which are crucial nutrients for the immune system. These deficiencies contribute to new waves of COVID-19 and can cause the infections to become life-threatening. The panel calls for immediate action with relevant focus on diet and supplements.
A panel of physicians and professors collaborating with the Swiss Society for Nutrition (SSN) recently reviewed the scientific evidence on the role of micronutrients in supporting a well-functioning immune defense for optimal health with particular focus on viral infections related to COVID-19. They conclude that there is widespread lack of vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids, all of which are crucial nutrients for the immune system. These deficiencies contribute to new waves of COVID-19 and can cause the infections to become life-threatening. The panel calls for immediate action with relevant focus on diet and supplements. Weight-challenged children and teenagers have grown to become a global health threat, and the problem became even worse during the corona pandemic. Overweight is linked to a number of health problems, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease that sets the stage for type 2 diabetes and other serious ailments. In a new review article that is published in Nutrients, researchers look closer at how a carbohydrate-restricted diet or the traditional Mediterranean diet can help to counteract the development of overweight and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Also, supplementation with vitamin E, vitamin D, fish oil, and probiotics can block the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver via different metabolic parameters.
Weight-challenged children and teenagers have grown to become a global health threat, and the problem became even worse during the corona pandemic. Overweight is linked to a number of health problems, including non-alcoholic fatty liver disease that sets the stage for type 2 diabetes and other serious ailments. In a new review article that is published in Nutrients, researchers look closer at how a carbohydrate-restricted diet or the traditional Mediterranean diet can help to counteract the development of overweight and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Also, supplementation with vitamin E, vitamin D, fish oil, and probiotics can block the development of non-alcoholic fatty liver via different metabolic parameters.
 Many men suffer from erectile dysfunction, a problem that often foreshadows cardiovascular disorders. It appears that
Many men suffer from erectile dysfunction, a problem that often foreshadows cardiovascular disorders. It appears that  Approximately one billion people worldwide lack
Approximately one billion people worldwide lack  At northern latitudes, our body can only produce
At northern latitudes, our body can only produce  Having healthy-looking hair means a lot to most people. Hair that splits at the ends, hair loss, and other hair problems may be caused by stress, hormone changes, and numerous other factors. In this article, we will take a closer look at the diet and its impact on hair health, and we will look at available studies of protein, iron, zinc, selenium, silica, B vitamins, vitamin D and vitamin A. The fact is, we need plenty of these nutrients in a form that the body can absorb and utilize. On the other hand, getting too much can do more harm than good, according to an article in Dermatology Practical & Conceptual, in which the author has analyzed the available research.
Having healthy-looking hair means a lot to most people. Hair that splits at the ends, hair loss, and other hair problems may be caused by stress, hormone changes, and numerous other factors. In this article, we will take a closer look at the diet and its impact on hair health, and we will look at available studies of protein, iron, zinc, selenium, silica, B vitamins, vitamin D and vitamin A. The fact is, we need plenty of these nutrients in a form that the body can absorb and utilize. On the other hand, getting too much can do more harm than good, according to an article in Dermatology Practical & Conceptual, in which the author has analyzed the available research. Research conducted over the past decades reveals that
Research conducted over the past decades reveals that  Most people have experienced a normal headache, while migraines are far more complex. Although the pain can be caused by a number of factors, essential nutrients such as B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 may play a vital role according to a review article that is published in Current Pain and Headache Reports. The authors describe how certain nutrients affect underlying mechanisms that may prevent or mitigate different types of headaches.
Most people have experienced a normal headache, while migraines are far more complex. Although the pain can be caused by a number of factors, essential nutrients such as B vitamins, vitamin D, magnesium, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 may play a vital role according to a review article that is published in Current Pain and Headache Reports. The authors describe how certain nutrients affect underlying mechanisms that may prevent or mitigate different types of headaches. Having sufficient
Having sufficient  The interplay between
The interplay between  Coronary occlusion is the leading cause of death worldwide. Type 2 diabetes is spreading like a bushfire and this disease is characterized by atherosclerosis and early death. Diet and lifestyle are of vital importance and the same goes for
Coronary occlusion is the leading cause of death worldwide. Type 2 diabetes is spreading like a bushfire and this disease is characterized by atherosclerosis and early death. Diet and lifestyle are of vital importance and the same goes for  The immune system cannot function without
The immune system cannot function without  Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, and our diet and lifestyle play a major role. According to an Australian study published in British Medical Journal, high-dosed
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, and our diet and lifestyle play a major role. According to an Australian study published in British Medical Journal, high-dosed
 Scientists have discussed for quite some time to what extent
Scientists have discussed for quite some time to what extent  Lack of
Lack of  Sales of plant-based meat, also known as meat analogue, has increased for environmental reasons and a number of other reasons. However, even if meat analogue does resemble regular animal meat it has an entirely different nutritional value. According to a study from Duke University in the United States, real meat contains 22 different nutrients and metabolites that you do not get from meat analogue. On the other hand, meat based on vegetarian sources contains 31 nutrients and metabolites that are not found in normal meat. The largest difference between the two, according to the scientists, lies in their content of amino acids, peptides, vitamins, phenols, and fatty acids. The researchers also mention that a diet based on vegetable and animal products is complementary because it contains more nutrients.
Sales of plant-based meat, also known as meat analogue, has increased for environmental reasons and a number of other reasons. However, even if meat analogue does resemble regular animal meat it has an entirely different nutritional value. According to a study from Duke University in the United States, real meat contains 22 different nutrients and metabolites that you do not get from meat analogue. On the other hand, meat based on vegetarian sources contains 31 nutrients and metabolites that are not found in normal meat. The largest difference between the two, according to the scientists, lies in their content of amino acids, peptides, vitamins, phenols, and fatty acids. The researchers also mention that a diet based on vegetable and animal products is complementary because it contains more nutrients.
 The mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells that churn out energy in a process that involves oxygen, Q10, selenium, and other nutrients. Around 100 years ago, the German Nobel Prize winner, Professor Otto Warburg, demonstrated that even if cancer can be caused by a number of secondary factors, there is only one primary cause: alterations in the mitochondrial oxygen turnover. In his recent book, Tripping over the Truth, molecular biologist Travis Christoffersen describes how contemporary scientists confirm Warburg’s theories and says that we need to look at prevention and cancer treatment from an entirely different angle. Other studies show that Parkinson’s disease, migraine, senility, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, epilepsy, and other neurological disorders may be rooted in defects of the mitochondria that have many other functions besides delivering energy. It is therefore vital to take care of the mitochondria throughout life. You can read more about the ketogenic diet that optimizes mitochondrial energy turnover in different mitochondrial diseases.
The mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells that churn out energy in a process that involves oxygen, Q10, selenium, and other nutrients. Around 100 years ago, the German Nobel Prize winner, Professor Otto Warburg, demonstrated that even if cancer can be caused by a number of secondary factors, there is only one primary cause: alterations in the mitochondrial oxygen turnover. In his recent book, Tripping over the Truth, molecular biologist Travis Christoffersen describes how contemporary scientists confirm Warburg’s theories and says that we need to look at prevention and cancer treatment from an entirely different angle. Other studies show that Parkinson’s disease, migraine, senility, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, epilepsy, and other neurological disorders may be rooted in defects of the mitochondria that have many other functions besides delivering energy. It is therefore vital to take care of the mitochondria throughout life. You can read more about the ketogenic diet that optimizes mitochondrial energy turnover in different mitochondrial diseases.
 Ageing is linked to uncontrolled, low-grade inflammation, also known as inflammaging, according to articles published in the journals Nature Medicine and Ageing and Disease. Although chronic inflammation is not felt directly it may set the stage for cardiovascular disease, rheumatism, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. Chronic inflammation may also cause virus infections like influenza and COVID-19 to become life-threatening because the immune defense suddenly overreacts and attacks healthy tissue. It is therefore vital for ageing people to protect themselves against chronic inflammation, which means getting plenty of vitamin D, selenium, coenzyme Q10, zinc, omega-3, and melatonin. These are all things that many older people often lack.
Ageing is linked to uncontrolled, low-grade inflammation, also known as inflammaging, according to articles published in the journals Nature Medicine and Ageing and Disease. Although chronic inflammation is not felt directly it may set the stage for cardiovascular disease, rheumatism, Alzheimer’s disease, and cancer. Chronic inflammation may also cause virus infections like influenza and COVID-19 to become life-threatening because the immune defense suddenly overreacts and attacks healthy tissue. It is therefore vital for ageing people to protect themselves against chronic inflammation, which means getting plenty of vitamin D, selenium, coenzyme Q10, zinc, omega-3, and melatonin. These are all things that many older people often lack.
 Insulin resistance is when the cells’ ability to take up glucose from the blood is impaired. It typically causes abnormal hunger and weight gain. Insulin resistance is also one of the symptoms of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Previous studies have already demonstrated a link between vitamin D deficiency and the development of insulin resistance. The risk is even greater if you also lack magnesium, according to an American study. Here, the researchers look at interactions between
Insulin resistance is when the cells’ ability to take up glucose from the blood is impaired. It typically causes abnormal hunger and weight gain. Insulin resistance is also one of the symptoms of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes. Previous studies have already demonstrated a link between vitamin D deficiency and the development of insulin resistance. The risk is even greater if you also lack magnesium, according to an American study. Here, the researchers look at interactions between  Irritable bowel is the most common intestinal disorder and affects around 15 percent of the population. The symptoms are typically unstable digestion, flatulence, constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, and intestinal cramps. Several studies have shown that lack of
Irritable bowel is the most common intestinal disorder and affects around 15 percent of the population. The symptoms are typically unstable digestion, flatulence, constipation, diarrhea, stomach pain, and intestinal cramps. Several studies have shown that lack of 
 Expecting mothers should pay careful attention to getting enough vitamin D all year round, especially because vitamin D deficiencies are so commonplace, to begin with. Lack of vitamin D at birth and the first years of life is associated with an increased risk of infant hypertension, and the problem can even continue to adulthood. This was shown in a study that is published in the science journal Hypertension. The researchers advise pregnant women to have their vitamin D levels measured, and they even recommend vitamin D supplements for pregnant women and children as a way of preventing elevated blood pressure later in life.
Expecting mothers should pay careful attention to getting enough vitamin D all year round, especially because vitamin D deficiencies are so commonplace, to begin with. Lack of vitamin D at birth and the first years of life is associated with an increased risk of infant hypertension, and the problem can even continue to adulthood. This was shown in a study that is published in the science journal Hypertension. The researchers advise pregnant women to have their vitamin D levels measured, and they even recommend vitamin D supplements for pregnant women and children as a way of preventing elevated blood pressure later in life. Scientists from Queensland in Australia have discovered that
Scientists from Queensland in Australia have discovered that  The number of children and adolescents with ADHD has skyrocketed in the past decade, and the human and socioeconomic costs are enormous. A major cause may be the widespread problems with vitamin D deficiency, according to a study from Turku University in Finland. It does not make things any easier that sun awareness campaigns fail to give people an alternative way of getting enough
The number of children and adolescents with ADHD has skyrocketed in the past decade, and the human and socioeconomic costs are enormous. A major cause may be the widespread problems with vitamin D deficiency, according to a study from Turku University in Finland. It does not make things any easier that sun awareness campaigns fail to give people an alternative way of getting enough 
 Vitamin D’s role in maintaining proper health is well documented. Still, many older people lack the nutrient and that increases their risk of bone fractures, blood poisoning, and disease complications that can eventually lead to hospitalization. Also, they risk prolonged hospitalization according to a new Irish study published in the scientific journal Nutrients. The scientists recommend giving vitamin D supplements to seniors to increase their blood levels of vitamin D. Other studies even suggest that this can protect against COVID-19, as low vitamin D status is associated with an increased risk of being hospitalized with the disease.
Vitamin D’s role in maintaining proper health is well documented. Still, many older people lack the nutrient and that increases their risk of bone fractures, blood poisoning, and disease complications that can eventually lead to hospitalization. Also, they risk prolonged hospitalization according to a new Irish study published in the scientific journal Nutrients. The scientists recommend giving vitamin D supplements to seniors to increase their blood levels of vitamin D. Other studies even suggest that this can protect against COVID-19, as low vitamin D status is associated with an increased risk of being hospitalized with the disease. Vitamin D-deficient experimental animals are more likely to become dependent on opioids such as morphine, but their addiction decreases once their blood levels of
Vitamin D-deficient experimental animals are more likely to become dependent on opioids such as morphine, but their addiction decreases once their blood levels of  Atrial fibrillation is a rhythm disturbance in the electrical system of the heart. It is also one of the most common heart disorders and can be both harmless and potentially life-threatening. Lack of
Atrial fibrillation is a rhythm disturbance in the electrical system of the heart. It is also one of the most common heart disorders and can be both harmless and potentially life-threatening. Lack of 
 Decades of research show that there is a link between lack of vitamin D and an increased risk of breast cancer. Vitamin D deficiencies are especially common at the northern latitudes because the sun sits too low in the sky for humans to be able to synthesize the vitamin during the winter. However, even in the southern hemisphere, many women have too little vitamin D because of spending too much time indoors, using too much suncream, or veiling themselves. Vitamin D has many anti-cancer properties, and postmenopausal women with too little vitamin D in their blood, who are diagnosed with breast cancer, have worse odds, according to a study of Brazilian women. In other words, it is not enough to treat breast cancer with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. You also need to optimize your blood levels of vitamin D and other nutrients, which the body needs in order to function optimally.
Decades of research show that there is a link between lack of vitamin D and an increased risk of breast cancer. Vitamin D deficiencies are especially common at the northern latitudes because the sun sits too low in the sky for humans to be able to synthesize the vitamin during the winter. However, even in the southern hemisphere, many women have too little vitamin D because of spending too much time indoors, using too much suncream, or veiling themselves. Vitamin D has many anti-cancer properties, and postmenopausal women with too little vitamin D in their blood, who are diagnosed with breast cancer, have worse odds, according to a study of Brazilian women. In other words, it is not enough to treat breast cancer with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiation. You also need to optimize your blood levels of vitamin D and other nutrients, which the body needs in order to function optimally.
 Hashimoto’s disease (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) is an overlooked scourge that leads to hypothyroidism and is particularly widespread among women. Postpartum thyroiditis that also slows down your metabolism follows in the wake of pregnancy. Graves’ disease where the metabolism speeds up (hyperthyroidism) is less common. These three thyroid disorders belong to the group of autoimmune disorders where the immune defense attacks the body’s tissues, and it appears that lack of
Hashimoto’s disease (Hashimoto’s thyroiditis) is an overlooked scourge that leads to hypothyroidism and is particularly widespread among women. Postpartum thyroiditis that also slows down your metabolism follows in the wake of pregnancy. Graves’ disease where the metabolism speeds up (hyperthyroidism) is less common. These three thyroid disorders belong to the group of autoimmune disorders where the immune defense attacks the body’s tissues, and it appears that lack of  A large Irish study has shown for the first time ever that people from 50 years of age and older, who are vitamin D-deficient, are more likely to develop depression.
A large Irish study has shown for the first time ever that people from 50 years of age and older, who are vitamin D-deficient, are more likely to develop depression. It is hardly a coincidence that sore throats, colds, flus, and related complications such as sinus infections and pneumonia typically circulate during the winter period. They are primarily a result of having low
It is hardly a coincidence that sore throats, colds, flus, and related complications such as sinus infections and pneumonia typically circulate during the winter period. They are primarily a result of having low  Type 2 diabetes is currently treated with a number of different medical drugs. However, the medicine is not able to deal with the underlying causes of the disease that affects most organ systems. A Chinese study has demonstrated that
Type 2 diabetes is currently treated with a number of different medical drugs. However, the medicine is not able to deal with the underlying causes of the disease that affects most organ systems. A Chinese study has demonstrated that  PCOS or polycystic ovary syndrome is a hormone imbalance and the most common cause of involuntary female infertility. The disease brings on symptoms such as tiredness, sugar cravings, overweight, hirsutism, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. It turns out that women with PCOS also have lower levels of
PCOS or polycystic ovary syndrome is a hormone imbalance and the most common cause of involuntary female infertility. The disease brings on symptoms such as tiredness, sugar cravings, overweight, hirsutism, and an increased risk of type 2 diabetes. It turns out that women with PCOS also have lower levels of  Get lots of sunlight. It is the richest source of
Get lots of sunlight. It is the richest source of  The most common inflammatory bowel diseases are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Lack of certain nutrients can contribute to the development of these conditions. On the other hand, the diseases and the therapies used to treat them may also impair the body’s ability to absorb or utilize certain nutrients, thereby starting a vicious cycle that can make the disease worse. This was demonstrated in a new Greek study that is published in Nutrients. Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases primarily occur in the Western countries and especially at northern latitudes, which suggests that sun exposure and typically Western diets pay a major role in the development of these diseases.
The most common inflammatory bowel diseases are Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis. Lack of certain nutrients can contribute to the development of these conditions. On the other hand, the diseases and the therapies used to treat them may also impair the body’s ability to absorb or utilize certain nutrients, thereby starting a vicious cycle that can make the disease worse. This was demonstrated in a new Greek study that is published in Nutrients. Chronic inflammatory bowel diseases primarily occur in the Western countries and especially at northern latitudes, which suggests that sun exposure and typically Western diets pay a major role in the development of these diseases. A large Israeli population study of over 4.6 million people shows that lack of sunshine and
A large Israeli population study of over 4.6 million people shows that lack of sunshine and  Girls with high blood levels of
Girls with high blood levels of  Menopause is characterized by a host of completely natural physiological changes in the hormonal balance. However, many women experience hormonal imbalances that may lead to weight gain, redistribution of their fat mass, increased abdominal obesity and an elevated risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and cancer. The hormonal changes may also affect the nutritional status including nutrients like
Menopause is characterized by a host of completely natural physiological changes in the hormonal balance. However, many women experience hormonal imbalances that may lead to weight gain, redistribution of their fat mass, increased abdominal obesity and an elevated risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, type 2 diabetes, and cancer. The hormonal changes may also affect the nutritional status including nutrients like  We need plenty of
We need plenty of  "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.