afterLoad (456.28KB) (7.16ms)
afterInitialise (1.27MB) (134ms)
afterRoute (840.61KB) (27.86ms)
beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.75KB) (6.38ms)
afterRenderComponent com_tags (2.92MB) (593ms)
afterDispatch (27.5KB) (2.19ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (443.86KB) (16.92ms)
Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (1.6ms)
After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (4.11ms)
Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (19μs)
After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (41μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (11.73KB) (176ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (23μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (157μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (14μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (23.16KB) (183ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (30μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (49μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (10μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (22μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (8μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (7μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (7μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (17μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (7μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (17μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (7μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (16μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (426μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (17μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (6ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (24μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (340μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (15μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (31μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (9.2ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (39μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (4μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (52μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (28μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (296μs)
afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (4.05ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (18μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (42μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (12μs)
afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (40μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (19μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (19μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (19μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (24μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (19μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (19μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (34μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (29.14KB) (2.21ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (186.95KB) (1.24ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (4μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (49μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (17μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (22.56KB) (8.61ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (19μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (10μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (7.44ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (34μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (138μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.67KB) (2.15ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (45μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (93μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (2.74ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (39μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (18μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (618μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (29μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (3.54ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (55μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (198μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (127μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (24μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (87μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (3.02ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (30μs)
afterRender (616.25KB) (16.72ms)
| 1 x afterRenderComponent com_tags (2.92MB) (48.43%) | 593.40ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (23.16KB) (14.96%) | 183.28ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (11.73KB) (14.37%) | 176.12ms |
| 1 x afterInitialise (1.27MB) (10.97%) | 134.37ms |
| 1 x afterRoute (840.61KB) (2.27%) | 27.86ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (443.86KB) (1.38%) | 16.92ms |
| 1 x afterRender (616.25KB) (1.36%) | 16.72ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (0.75%) | 9.20ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (22.56KB) (0.7%) | 8.61ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (0.61%) | 7.44ms |
| 1 x afterLoad (456.28KB) (0.58%) | 7.16ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.75KB) (0.52%) | 6.38ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (0.49%) | 6.00ms |
| 1 x After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (0.34%) | 4.11ms |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (0.33%) | 4.05ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (0.29%) | 3.54ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (0.25%) | 3.02ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (0.22%) | 2.74ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (29.14KB) (0.18%) | 2.21ms |
| 1 x afterDispatch (27.5KB) (0.18%) | 2.19ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.67KB) (0.18%) | 2.15ms |
| 1 x Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (0.13%) | 1.60ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (186.95KB) (0.1%) | 1.24ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (0.05%) | 618μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (0.03%) | 426μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (0.03%) | 340μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (0.02%) | 296μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (0.02%) | 198μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (0.01%) | 157μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (0.01%) | 138μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (0.01%) | 127μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (0.01%) | 93μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (0.01%) | 87μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (0%) | 55μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (0%) | 52μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (0%) | 49μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (0%) | 49μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (0%) | 45μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (0%) | 42μs |
| 1 x After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (0%) | 41μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (0%) | 40μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (0%) | 39μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (0%) | 39μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (0%) | 34μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (0%) | 34μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (0%) | 31μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (0%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (0%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (0%) | 29μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (0%) | 28μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (0%) | 24μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (0%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (0%) | 24μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (0%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (0%) | 20μs |
| 1 x Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (0%) | 17μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (0%) | 17μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (0%) | 17μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (0%) | 17μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (0%) | 16μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (0%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 3 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (0%) | 12μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (0%) | 5μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (0%) | 4μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (0%) | 3μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (0%) | 2μs |
 Molybdenum is essential for liver detoxification and plays a key role in breaking down proteins, purines, and lipids. It also supports the synthesis of vitamin B12. Studies even suggest that a molybdenum deficiency or poor utilization of the nutrient increases the risk of gout, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and hepatocellular carcinoma, which is a type of liver cancer.
Molybdenum is essential for liver detoxification and plays a key role in breaking down proteins, purines, and lipids. It also supports the synthesis of vitamin B12. Studies even suggest that a molybdenum deficiency or poor utilization of the nutrient increases the risk of gout, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), and hepatocellular carcinoma, which is a type of liver cancer.







 It is not the actual COVID-19 virus that can become lethal. It is the immune system’s overreaction with hyperinflammation and a storm of cytokines that destroys healthy tissue in the lungs, the cardiovascular system, and other places in the body, according to a new article that is published in The Lancet. The capacity of the immune system determines if an infection like COVID-19 is either harmless or life-threatening. For that reason, hygienic measures, masks, isolation, and delayed vaccines are not sufficient. We also need to bolster our immune system against COVID-19 and other pandemics that may occur in the future. Let’s look closer at vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium and zinc, all of which are essential for preventing a well-functioning immune system from going off its rails. What is also worth mentioning is that many people lack these nutrients, especially older people and other exposed groups.
It is not the actual COVID-19 virus that can become lethal. It is the immune system’s overreaction with hyperinflammation and a storm of cytokines that destroys healthy tissue in the lungs, the cardiovascular system, and other places in the body, according to a new article that is published in The Lancet. The capacity of the immune system determines if an infection like COVID-19 is either harmless or life-threatening. For that reason, hygienic measures, masks, isolation, and delayed vaccines are not sufficient. We also need to bolster our immune system against COVID-19 and other pandemics that may occur in the future. Let’s look closer at vitamin C, vitamin D, selenium and zinc, all of which are essential for preventing a well-functioning immune system from going off its rails. What is also worth mentioning is that many people lack these nutrients, especially older people and other exposed groups.
 Alcohol has a greater negative impact on public health than most other things. It is commonly known that alcohol abuse burdens the liver and depletes the body of B vitamins. Now, scientists have also demonstrated that overconsumption of alcohol leaches
Alcohol has a greater negative impact on public health than most other things. It is commonly known that alcohol abuse burdens the liver and depletes the body of B vitamins. Now, scientists have also demonstrated that overconsumption of alcohol leaches  Antioxidants such as
Antioxidants such as  Antioxidants such as vitamins C and E are known to be inversely related to type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disease. In a new Swedish study that is published in Nutrients, scientists have found that vitamin E also protects against type 1,5 diabetes, which is similar to type 1 and type 2 diabetes because it involves both autoimmune reactions and insulin resistance. The scientists list different foods that are rich in vitamin E and also describe how vitamin E protects the pancreas against autoimmune attacks and oxidative stress.
Antioxidants such as vitamins C and E are known to be inversely related to type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disease. In a new Swedish study that is published in Nutrients, scientists have found that vitamin E also protects against type 1,5 diabetes, which is similar to type 1 and type 2 diabetes because it involves both autoimmune reactions and insulin resistance. The scientists list different foods that are rich in vitamin E and also describe how vitamin E protects the pancreas against autoimmune attacks and oxidative stress. It is estimated that one billion people worldwide lack
It is estimated that one billion people worldwide lack  We all know that calcium is good for your bones, and many people actually supplement with calcium to prevent osteoporosis. But even without supplementation, we get plenty of
We all know that calcium is good for your bones, and many people actually supplement with calcium to prevent osteoporosis. But even without supplementation, we get plenty of  Yes, according to a new study published in Free Radical Biology & Medicine, lack of
Yes, according to a new study published in Free Radical Biology & Medicine, lack of  There is a clear link between
There is a clear link between  This almost sounds too good to be true, but scientists from Germany and the United States have discovered that
This almost sounds too good to be true, but scientists from Germany and the United States have discovered that  Everyone is affected by electromagnetic radiation from cell phones, device screens, the electricity supply and other electric systems. The brain’s neurons are particularly vulnerable, especially because electromagnetic radiation can increase the neuronal uptake of calcium ions, which makes the neurons overactive and may even cause them to perish. A study published in News Medical Life Sciences shows that too much calcium in the brain increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and digital dementia in young individuals. The increased electromagnetic radiation also generates loads of free radicals in the body that can cause oxidative stress and cellular damage because it outperforms the body’s different antioxidants. This was described in an article published in The Journal of Microscopy & Ultrastructure that also mentions how electromagnetic radiation can cause stress, headaches, fatigue, anxiety, and other symptoms.
Everyone is affected by electromagnetic radiation from cell phones, device screens, the electricity supply and other electric systems. The brain’s neurons are particularly vulnerable, especially because electromagnetic radiation can increase the neuronal uptake of calcium ions, which makes the neurons overactive and may even cause them to perish. A study published in News Medical Life Sciences shows that too much calcium in the brain increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and digital dementia in young individuals. The increased electromagnetic radiation also generates loads of free radicals in the body that can cause oxidative stress and cellular damage because it outperforms the body’s different antioxidants. This was described in an article published in The Journal of Microscopy & Ultrastructure that also mentions how electromagnetic radiation can cause stress, headaches, fatigue, anxiety, and other symptoms. The coronavirus has spread from Wuhan in China to a number of continents, where it has caused massive fear and affected daily life and the global economy. Although most people that get the infection experience a mild course of events, the greatest fear is the potentially life-threatening complications in the respiratory system caused by oxidative stress, which have already taken thousands of human lives. Chinese scientists now call for early intravenous therapy with large doses of vitamin C to prevent oxidative stress and the life-threatening complications that follow in the wake of a derailed immune system. Many researchers also claim that higher intake of vitamin C from dietary sources or supplements help prevent by boosting and regulating the immune system in the upper respiratory tract. The same goes for vitamin D and selenium.
The coronavirus has spread from Wuhan in China to a number of continents, where it has caused massive fear and affected daily life and the global economy. Although most people that get the infection experience a mild course of events, the greatest fear is the potentially life-threatening complications in the respiratory system caused by oxidative stress, which have already taken thousands of human lives. Chinese scientists now call for early intravenous therapy with large doses of vitamin C to prevent oxidative stress and the life-threatening complications that follow in the wake of a derailed immune system. Many researchers also claim that higher intake of vitamin C from dietary sources or supplements help prevent by boosting and regulating the immune system in the upper respiratory tract. The same goes for vitamin D and selenium. There is a link between depression, dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Also, it appears that chronic stress contributes to oxidative stress and brain cell damage. In a review article that is published in the science journal Antioxidants, researchers look closer at how oxidative stress affects the brain. They also study how antioxidants can be included in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, and why the most promising results are seen with selenium, Q10, melatonin, vitamin E, turmeric, and polyphenols. With regard to depression, selenium, zinc, vitamin E, turmeric, and saffron have demonstrated the greatest potential.
There is a link between depression, dementia and Alzheimer’s disease. Also, it appears that chronic stress contributes to oxidative stress and brain cell damage. In a review article that is published in the science journal Antioxidants, researchers look closer at how oxidative stress affects the brain. They also study how antioxidants can be included in the prevention and treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, and why the most promising results are seen with selenium, Q10, melatonin, vitamin E, turmeric, and polyphenols. With regard to depression, selenium, zinc, vitamin E, turmeric, and saffron have demonstrated the greatest potential.
 Many men suffer from erectile dysfunction, a problem that often foreshadows cardiovascular disorders. It appears that
Many men suffer from erectile dysfunction, a problem that often foreshadows cardiovascular disorders. It appears that  The majority of sexually active people contract HPV (human papilloma virus), of which there are several types. Normally, the infection goes away by itself but in some cases it becomes chronic. This increases the risk of serious cell changes in the cervix which, in worst case, can result in cervical cancer. An American study has found that having adequate levels of five different antioxidants – albumin plus vitamins A, B2, E, and folic acid – may lower papilloma virus infections that are linked to cervical cancer.
The majority of sexually active people contract HPV (human papilloma virus), of which there are several types. Normally, the infection goes away by itself but in some cases it becomes chronic. This increases the risk of serious cell changes in the cervix which, in worst case, can result in cervical cancer. An American study has found that having adequate levels of five different antioxidants – albumin plus vitamins A, B2, E, and folic acid – may lower papilloma virus infections that are linked to cervical cancer. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a liver disease that is spreading like a bushfire. NAFLD is associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, which is an early stage of type 2 diabetes. What you eat plays a major role, and a large Chinese study has actually demonstrated that higher dietary intake of
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a liver disease that is spreading like a bushfire. NAFLD is associated with obesity and metabolic syndrome, which is an early stage of type 2 diabetes. What you eat plays a major role, and a large Chinese study has actually demonstrated that higher dietary intake of 
 The mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells that churn out energy in a process that involves oxygen, Q10, selenium, and other nutrients. Around 100 years ago, the German Nobel Prize winner, Professor Otto Warburg, demonstrated that even if cancer can be caused by a number of secondary factors, there is only one primary cause: alterations in the mitochondrial oxygen turnover. In his recent book, Tripping over the Truth, molecular biologist Travis Christoffersen describes how contemporary scientists confirm Warburg’s theories and says that we need to look at prevention and cancer treatment from an entirely different angle. Other studies show that Parkinson’s disease, migraine, senility, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, epilepsy, and other neurological disorders may be rooted in defects of the mitochondria that have many other functions besides delivering energy. It is therefore vital to take care of the mitochondria throughout life. You can read more about the ketogenic diet that optimizes mitochondrial energy turnover in different mitochondrial diseases.
The mitochondria are the powerhouses of our cells that churn out energy in a process that involves oxygen, Q10, selenium, and other nutrients. Around 100 years ago, the German Nobel Prize winner, Professor Otto Warburg, demonstrated that even if cancer can be caused by a number of secondary factors, there is only one primary cause: alterations in the mitochondrial oxygen turnover. In his recent book, Tripping over the Truth, molecular biologist Travis Christoffersen describes how contemporary scientists confirm Warburg’s theories and says that we need to look at prevention and cancer treatment from an entirely different angle. Other studies show that Parkinson’s disease, migraine, senility, chronic fatigue, fibromyalgia, epilepsy, and other neurological disorders may be rooted in defects of the mitochondria that have many other functions besides delivering energy. It is therefore vital to take care of the mitochondria throughout life. You can read more about the ketogenic diet that optimizes mitochondrial energy turnover in different mitochondrial diseases. Chronic fatigue commonly follows in the wake of influenza, herpes, COVID-19, and other infections. The immune system does not function optimally, and the tiredness is caused by oxidative stress and inflammation. The condition is often accompanied by poor concentration, depression, and sleep disturbances. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between pro-inflammatory free radicals and protective antioxidants.
Chronic fatigue commonly follows in the wake of influenza, herpes, COVID-19, and other infections. The immune system does not function optimally, and the tiredness is caused by oxidative stress and inflammation. The condition is often accompanied by poor concentration, depression, and sleep disturbances. Oxidative stress is an imbalance between pro-inflammatory free radicals and protective antioxidants.  Critically ill patients often suffer from inflammation and oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between harmful free radicals and protective antioxidants. In worst case, this may result in tissue damage and organ failure. It turns out
Critically ill patients often suffer from inflammation and oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between harmful free radicals and protective antioxidants. In worst case, this may result in tissue damage and organ failure. It turns out  Perhaps so. More and more studies reveal that it helps to take large quantities of
Perhaps so. More and more studies reveal that it helps to take large quantities of 
 Kidney stones is a painful and quite common problem. The diet plays a major role and according to a large American population study published in Nutrients,
Kidney stones is a painful and quite common problem. The diet plays a major role and according to a large American population study published in Nutrients,  When it comes to COVID-19 and other seasonal virus infections most of the focus is concentrated on vitamin D deficiency. According to a Belgian study, however, lack of selenium and zinc additionally increases the risk of infections, complications, and death, especially among patients who already suffer from chronic diseases. The scientists conclude that supplementation with selenium and zinc may help improve treatments. Selenium and zinc deficiencies are rather common and that is a problem for public health. Even with a healthy diet, it is practically impossible for Europeans to get enough selenium because of the nutrient-depleted farmland. There are also many people with zinc deficiencies due to unhealthy diets, ageing, chronic diseases, and other contributing factors. We must be much more focused on getting enough selenium and zinc, not least for the sake of preventing virus infections and other problems.
When it comes to COVID-19 and other seasonal virus infections most of the focus is concentrated on vitamin D deficiency. According to a Belgian study, however, lack of selenium and zinc additionally increases the risk of infections, complications, and death, especially among patients who already suffer from chronic diseases. The scientists conclude that supplementation with selenium and zinc may help improve treatments. Selenium and zinc deficiencies are rather common and that is a problem for public health. Even with a healthy diet, it is practically impossible for Europeans to get enough selenium because of the nutrient-depleted farmland. There are also many people with zinc deficiencies due to unhealthy diets, ageing, chronic diseases, and other contributing factors. We must be much more focused on getting enough selenium and zinc, not least for the sake of preventing virus infections and other problems. Millions of people take painkillers such as Panadol or Calpol that contain paracetamol, and an estimated one billion people or so lack
Millions of people take painkillers such as Panadol or Calpol that contain paracetamol, and an estimated one billion people or so lack 
 It is commonly known that pregnant diabetics have an increased risk of developing an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. The diet plays a major role and it appears that a
It is commonly known that pregnant diabetics have an increased risk of developing an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. The diet plays a major role and it appears that a 
 Elevated blood pressure is the main cause of stroke, cardiovascular disease and early death. For quite some time, there has been evidence that intake of fruit and vegetables affects the risk of developing elevated blood pressure. Science has not yet studied if this is due to the antioxidants in our diets, but a team of French scientists has looked closer at this. The researchers found that the total amount of antioxidants in our diet may lower by 15 percent the risk of elevated blood pressure. The potassium in fruit and vegetables also play a determining role in blood pressure management, and the same goes for Q10 – provided you take quality supplements with proper absorption.
Elevated blood pressure is the main cause of stroke, cardiovascular disease and early death. For quite some time, there has been evidence that intake of fruit and vegetables affects the risk of developing elevated blood pressure. Science has not yet studied if this is due to the antioxidants in our diets, but a team of French scientists has looked closer at this. The researchers found that the total amount of antioxidants in our diet may lower by 15 percent the risk of elevated blood pressure. The potassium in fruit and vegetables also play a determining role in blood pressure management, and the same goes for Q10 – provided you take quality supplements with proper absorption. Melatonin is primarily known as a sleep hormone and a powerful antioxidant. According to a new study, melatonin may even improve the condition of rats that have heart rhythm disturbances with an increased risk of heart attack. Melatonin’s ability to improve the heart function is not related to its antioxidant function, however, and that surprised the scientists behind the study. The new study was presented at an annual meeting for the American Physiological Society (APS) in Orlando. Melatonin has several vital functions, but as we age our endogenous production decreases. Not only does this affect our quality of sleep, it also has a negative impact on the heart and the body’s cells.
Melatonin is primarily known as a sleep hormone and a powerful antioxidant. According to a new study, melatonin may even improve the condition of rats that have heart rhythm disturbances with an increased risk of heart attack. Melatonin’s ability to improve the heart function is not related to its antioxidant function, however, and that surprised the scientists behind the study. The new study was presented at an annual meeting for the American Physiological Society (APS) in Orlando. Melatonin has several vital functions, but as we age our endogenous production decreases. Not only does this affect our quality of sleep, it also has a negative impact on the heart and the body’s cells. Hereditary hemochromatosis is a group of diseases that involve iron accumulation in the body. This leads to oxidative stress and tissue destruction which may affect the liver and other organs. According to a new Argentinian study, patients with hereditary hemochromatosis lack
Hereditary hemochromatosis is a group of diseases that involve iron accumulation in the body. This leads to oxidative stress and tissue destruction which may affect the liver and other organs. According to a new Argentinian study, patients with hereditary hemochromatosis lack 
 Cardiovascular diseases are widespread and one of the major causes of death. The risk is increased by factors such as ageing, diabetes, and overweight. One of the underlying causes is oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants.
Cardiovascular diseases are widespread and one of the major causes of death. The risk is increased by factors such as ageing, diabetes, and overweight. One of the underlying causes is oxidative stress, which is an imbalance between free radicals and antioxidants. 
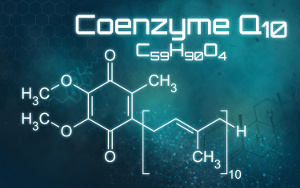 According to WHO, sepsis is the third-most common cause of death, following cardiovascular disease and death. Sepsis is a result of the immune defense overreacting to an infection in the bloodstream. According to a new Slovakian study published in Bratislava Medical Journal, if you start supplementing with
According to WHO, sepsis is the third-most common cause of death, following cardiovascular disease and death. Sepsis is a result of the immune defense overreacting to an infection in the bloodstream. According to a new Slovakian study published in Bratislava Medical Journal, if you start supplementing with 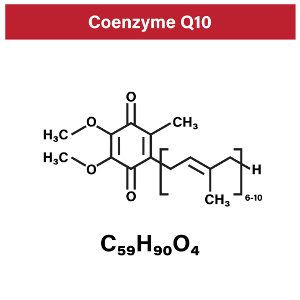 The body uses inflammation as part of its normal immune response to infections and tissue damage. If inflammation becomes chronic, however, it can be extremely dangerous. What happens is that it bombards the body with free radicals. This leads to oxidative stress and increases the risk of cell damage, overweight, and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, and different cancer forms. Diet and lifestyle play a major role, and according to a meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Pharmacology,
The body uses inflammation as part of its normal immune response to infections and tissue damage. If inflammation becomes chronic, however, it can be extremely dangerous. What happens is that it bombards the body with free radicals. This leads to oxidative stress and increases the risk of cell damage, overweight, and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, and different cancer forms. Diet and lifestyle play a major role, and according to a meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Pharmacology, 

 Rheumatism is the most widespread chronic disease in Denmark, and many people experience a worsening of the symptoms during the winter period. The majority of people take anti-inflammatory drugs for years, but this increases their risk of bleeding stomach ulcers and other side effects, not to mention premature death. The underlying cause is chronic inflammation and it is a problem that is not properly addressed. For decades, Nobel Prize-winners and other scientists have revealed what causes chronic inflammation and how the problem in many cases can be helped with various supplements that help cure the pain. In the following, we have summarized a lot of the research that has been conducted with vitamin D, fish oil, magnesium, selenium, zinc, and glucosamine, and we have looked at why the anti-inflammatory lifestyle has become such a health trend. It is essential to use supplements that contain the different ingredients in therapeutic doses and with a quality that allows the body to absorb and utilize the active compounds.
Rheumatism is the most widespread chronic disease in Denmark, and many people experience a worsening of the symptoms during the winter period. The majority of people take anti-inflammatory drugs for years, but this increases their risk of bleeding stomach ulcers and other side effects, not to mention premature death. The underlying cause is chronic inflammation and it is a problem that is not properly addressed. For decades, Nobel Prize-winners and other scientists have revealed what causes chronic inflammation and how the problem in many cases can be helped with various supplements that help cure the pain. In the following, we have summarized a lot of the research that has been conducted with vitamin D, fish oil, magnesium, selenium, zinc, and glucosamine, and we have looked at why the anti-inflammatory lifestyle has become such a health trend. It is essential to use supplements that contain the different ingredients in therapeutic doses and with a quality that allows the body to absorb and utilize the active compounds. The cells in our body are constantly renewed but they can only divide a limited number of times. It all depends on the length of their telomeres, which one can compare to the protective plastic tips at the ends of shoelaces. Every time a cell divides, its telomeres are reduced in length, bringing the cell closer to its terminal phase. Now, a Chinese study has revealed that higher
The cells in our body are constantly renewed but they can only divide a limited number of times. It all depends on the length of their telomeres, which one can compare to the protective plastic tips at the ends of shoelaces. Every time a cell divides, its telomeres are reduced in length, bringing the cell closer to its terminal phase. Now, a Chinese study has revealed that higher  It’s commonly known that physical activity boosts the brain’s ability to form new brain cells – or neurons. Still, the underlying mechanisms have been a mystery to science. A team of Australian scientists, however, has recently discovered that, during exercise, mice produce a selenium-containing protein that helps the brain synthesize new brain cells. The scientists consider this to be a rather fantastic study, and it is assumed that
It’s commonly known that physical activity boosts the brain’s ability to form new brain cells – or neurons. Still, the underlying mechanisms have been a mystery to science. A team of Australian scientists, however, has recently discovered that, during exercise, mice produce a selenium-containing protein that helps the brain synthesize new brain cells. The scientists consider this to be a rather fantastic study, and it is assumed that 
 Cataracts is one of the leading causes of vision impairment and blindness. The risk is increased by old age and diabetes. According to a new study that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, a relatively high
Cataracts is one of the leading causes of vision impairment and blindness. The risk is increased by old age and diabetes. According to a new study that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, a relatively high 
 The corona crisis has shed new light on the importance of having a strong immune defense, one that protects us against virus infections in the long run. Selenium plays a vital role for a number of different reasons but, unfortunately, there is widespread deficiency which increases the risk of infections and related complications. In a new review article that is published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences, the authors look closer at selenium’s role in connection with different types of virus infections such as influenza, HIV, and hepatitis with particular focus on COVID-19. The purpose of their article is to inform about new nutritional strategies that may contribute to a strong and well-functioning immune defense – mainly when it comes to COVID-19 and virus types that tend to mutate all the time.
The corona crisis has shed new light on the importance of having a strong immune defense, one that protects us against virus infections in the long run. Selenium plays a vital role for a number of different reasons but, unfortunately, there is widespread deficiency which increases the risk of infections and related complications. In a new review article that is published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences, the authors look closer at selenium’s role in connection with different types of virus infections such as influenza, HIV, and hepatitis with particular focus on COVID-19. The purpose of their article is to inform about new nutritional strategies that may contribute to a strong and well-functioning immune defense – mainly when it comes to COVID-19 and virus types that tend to mutate all the time.
 Everyone knows that exercise and sports activities are good for you, but overtraining and high-performance sport may increase your risk of oxidative stress, which is associated with acute injuries, inflammation and later risk of neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease and ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). It is therefore a good idea to take antioxidant supplements, as this may help prevent both acute and chronic injuries. A comprehensive article published in the science journal Nutrients looks closer at the relation between free radicals and antioxidants, which have different functions in connection with various types of physical activity. This is especially the case with vitamins A, C, and E plus selenium and zinc. It is also important to make sure to get enough vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids for counteracting inflammation and oxidative stress.
Everyone knows that exercise and sports activities are good for you, but overtraining and high-performance sport may increase your risk of oxidative stress, which is associated with acute injuries, inflammation and later risk of neurodegenerative disease such as Alzheimer’s disease and ALS (amyotrophic lateral sclerosis). It is therefore a good idea to take antioxidant supplements, as this may help prevent both acute and chronic injuries. A comprehensive article published in the science journal Nutrients looks closer at the relation between free radicals and antioxidants, which have different functions in connection with various types of physical activity. This is especially the case with vitamins A, C, and E plus selenium and zinc. It is also important to make sure to get enough vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids for counteracting inflammation and oxidative stress. Regular sport is good for you, whereas arduous training and high-performance sport can result in physical injuries, infections, chronic inflammation, and serious diseases due to oxidative stress. This phenomenon occurs as a result of the increased energy turnover, which produces an excess of free radicals that cause damage to cells and tissues. Oxidative stress is also associated with impaired performance, poor restitution, and faster ageing. Our only natural defense against free radicals is the presence of antioxidants, and it is especially things like
Regular sport is good for you, whereas arduous training and high-performance sport can result in physical injuries, infections, chronic inflammation, and serious diseases due to oxidative stress. This phenomenon occurs as a result of the increased energy turnover, which produces an excess of free radicals that cause damage to cells and tissues. Oxidative stress is also associated with impaired performance, poor restitution, and faster ageing. Our only natural defense against free radicals is the presence of antioxidants, and it is especially things like  The kidneys cleanse our blood. Well-functioning kidneys are vital for the circulatory system and good health in general. Normal functioning of cells, including kidney cells, hinges on a host of different selenium-containing proteins and coenzyme Q10. Studies show that older people in many parts of the world, Europe included, have deficiencies of both substances. Therefore, a team of Swedish scientists conducted a study where they looked at selenium status and kidney function in a group of seniors. They gave selenium yeast and coenzyme Q10 or placebo to the participants for a period of four years. The results showed that the supplemented group as compared with the placebo group had improved kidney function according to several parameters. The positive effect on cellular energy metabolism, inflammation, and oxidative stress was attributed to the two supplements. The study is published in the science journal Nutrients.
The kidneys cleanse our blood. Well-functioning kidneys are vital for the circulatory system and good health in general. Normal functioning of cells, including kidney cells, hinges on a host of different selenium-containing proteins and coenzyme Q10. Studies show that older people in many parts of the world, Europe included, have deficiencies of both substances. Therefore, a team of Swedish scientists conducted a study where they looked at selenium status and kidney function in a group of seniors. They gave selenium yeast and coenzyme Q10 or placebo to the participants for a period of four years. The results showed that the supplemented group as compared with the placebo group had improved kidney function according to several parameters. The positive effect on cellular energy metabolism, inflammation, and oxidative stress was attributed to the two supplements. The study is published in the science journal Nutrients. The blood supply to the retina of the eye is crucial for good vision. For that reason, experts recommend taking antioxidant supplements against eye diseases caused by an impaired blood supply to the retina. Although there is lacking evidence for the effectiveness of such supplements it appears now that Q10 and other antioxidants may improve vision when used in combination with conventional therapies, according to a Spanish study that is published in Nutrients. Because the body has difficulty with absorbing Q10 from supplements it is important to choose a supplement that has good bioavailability.
The blood supply to the retina of the eye is crucial for good vision. For that reason, experts recommend taking antioxidant supplements against eye diseases caused by an impaired blood supply to the retina. Although there is lacking evidence for the effectiveness of such supplements it appears now that Q10 and other antioxidants may improve vision when used in combination with conventional therapies, according to a Spanish study that is published in Nutrients. Because the body has difficulty with absorbing Q10 from supplements it is important to choose a supplement that has good bioavailability.
 Both physical traumas and critical illnesses are associated with inflammation and oxidative stress where free radicals can cause potentially life-threatening damage to cells and tissues. Traumas are estimated to be the cause of one in ten deaths. New research suggests that early intervention with
Both physical traumas and critical illnesses are associated with inflammation and oxidative stress where free radicals can cause potentially life-threatening damage to cells and tissues. Traumas are estimated to be the cause of one in ten deaths. New research suggests that early intervention with  Most people think of vitamin C in connection with the immune defense, but as it turns out, the largest concentration of
Most people think of vitamin C in connection with the immune defense, but as it turns out, the largest concentration of 
 Air pollution is a serious health threat that affects the entire world. Previous studies show that it increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, among other things. We need new strategies for protection, and a recent Chinese study conveniently reveals that supplementation with
Air pollution is a serious health threat that affects the entire world. Previous studies show that it increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, among other things. We need new strategies for protection, and a recent Chinese study conveniently reveals that supplementation with Telomeres are protective caps at the end of our DNA strands. You can compare them to the small plastic aglets that prevent shoelaces from unraveling. For each time a cell divides, the telomeres become shorter. The length of telomeres conveniently indicates our biological age. Diet plays a role and according to a large population study, vitamin C intake is linked to telomere length. The same is the case with Q10 and selenium, according to Swedish research. Vitamin C, Q10, and selenium serve as unique antioxidants that protect the telomeres and the cells against damage caused by oxidative stress.
Telomeres are protective caps at the end of our DNA strands. You can compare them to the small plastic aglets that prevent shoelaces from unraveling. For each time a cell divides, the telomeres become shorter. The length of telomeres conveniently indicates our biological age. Diet plays a role and according to a large population study, vitamin C intake is linked to telomere length. The same is the case with Q10 and selenium, according to Swedish research. Vitamin C, Q10, and selenium serve as unique antioxidants that protect the telomeres and the cells against damage caused by oxidative stress. PMS (premenstrual syndrome) is quite common among women of childbearing age and can easily make their lives miserable for years, causing both physical and mental discomfort several days a month. A possible cause can be lack of
PMS (premenstrual syndrome) is quite common among women of childbearing age and can easily make their lives miserable for years, causing both physical and mental discomfort several days a month. A possible cause can be lack of  According to an article that is published in StatPearls,
According to an article that is published in StatPearls,  It has been known for long that
It has been known for long that  Our ability to absorb
Our ability to absorb  Lack of dietary
Lack of dietary  We have relatively large quantities of
We have relatively large quantities of  "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.