| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (9.23KB) (30.24%) | 91.30ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (3.44KB) (24.48%) | 73.91ms |
| 1 x afterRenderComponent com_tags (1.46MB) (19.44%) | 58.70ms |
| 1 x afterInitialise (1.28MB) (8.53%) | 25.77ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (440.48KB) (4.26%) | 12.87ms |
| 1 x afterRoute (826.27KB) (2.59%) | 7.81ms |
| 1 x afterRender (242.66KB) (1.78%) | 5.38ms |
| 1 x afterDispatch (27.38KB) (1.07%) | 3.23ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (244.28KB) (0.76%) | 2.29ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (128.59KB) (0.68%) | 2.06ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (28.16KB) (0.63%) | 1.91ms |
| 1 x afterLoad (455.92KB) (0.59%) | 1.79ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.61KB) (0.54%) | 1.63ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (186.95KB) (0.52%) | 1.59ms |
| 1 x After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (0.51%) | 1.55ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.62KB) (0.38%) | 1.14ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (0.28%) | 858μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (6.3KB) (0.27%) | 823μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (29.14KB) (0.24%) | 727μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (0.23%) | 701μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (22.39KB) (0.22%) | 662μs |
| 1 x Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (50.9KB) (0.18%) | 534μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (20.82KB) (0.13%) | 394μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (25.52KB) (0.11%) | 327μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (17.83KB) (0.08%) | 244μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (3.8KB) (0.07%) | 204μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (0.07%) | 198μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (0.06%) | 186μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (0.05%) | 164μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (5.07KB) (0.05%) | 149μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (0.03%) | 105μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (0.03%) | 99μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (0.03%) | 94μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (1.25KB) (0.03%) | 78μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (0.02%) | 74μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.06KB) (0.02%) | 66μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (4.86KB) (0.02%) | 64μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (0.02%) | 58μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.55KB) (0.02%) | 57μs |
| 1 x After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (0.02%) | 54μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (3.29KB) (0.01%) | 44μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 43μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (816B) (0.01%) | 38μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.45KB) (0.01%) | 35μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.02KB) (0.01%) | 33μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 32μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (0.01%) | 31μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 31μs |
| 1 x Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (0.01%) | 28μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (0.01%) | 27μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (0.01%) | 27μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 25μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (960B) (0.01%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.06KB) (0.01%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (0.01%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (1.31KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (3.77KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (736B) (0.01%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (928B) (0.01%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (0.01%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (1.03KB) (0.01%) | 18μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.94KB) (0.01%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (912B) (0.01%) | 17μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (2.36KB) (0.01%) | 16μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.06KB) (0%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (6.81KB) (0%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (720B) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (0%) | 14μs |
| 3 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (0%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.5KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.98KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Are you getting enough vitamins and minerals?) (2.13KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (768B) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (608B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (The key to increased well-being) (352B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Overview of vitamins, minerals, and essential fatty acids) (384B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Q10 goes by many names) (208B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Weight loss that works) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Did you know.....) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Useful Links) (1.44KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.17KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main Menu - English) (720B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (0%) | 6μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (0%) | 3μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (0%) | 2μs |
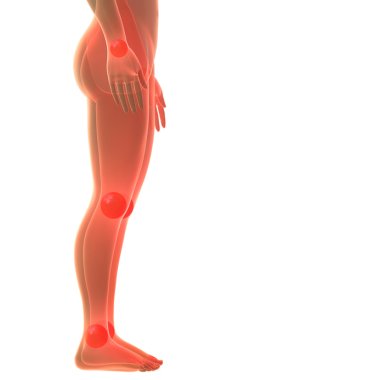 Choose natural solutions instead of potentially lethal medicine
Choose natural solutions instead of potentially lethal medicine







 A group of leading international experts (ESCEO) says in a new report that glucosamine sulfate in a pharmaceutical grade is safe and effective in the treatment of osteoarthritis and that it can be recommended as a basic treatment of this disorder. Also chondroitin is recommended
A group of leading international experts (ESCEO) says in a new report that glucosamine sulfate in a pharmaceutical grade is safe and effective in the treatment of osteoarthritis and that it can be recommended as a basic treatment of this disorder. Also chondroitin is recommended
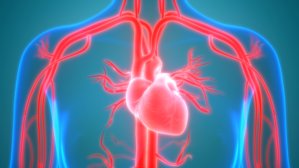 Patients who take glucosamine for their osteoarthritis have a bonus effect: The preparation also lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease, according to a large population study published in the science journal British Medical Journal. Always choose pharmaceutical-grade glucosamine so you are sure to obtain the desired effect.
Patients who take glucosamine for their osteoarthritis have a bonus effect: The preparation also lowers the risk of cardiovascular disease, according to a large population study published in the science journal British Medical Journal. Always choose pharmaceutical-grade glucosamine so you are sure to obtain the desired effect.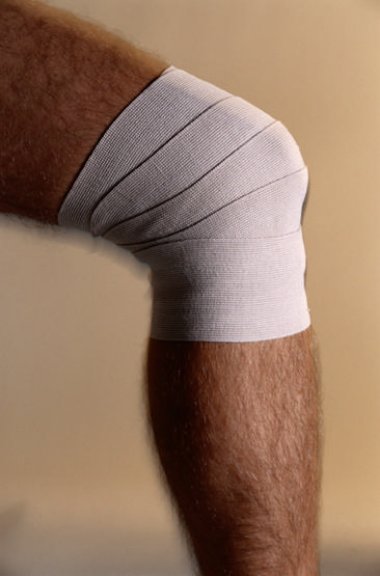 Combined supplementation with chondroitin sulphate and glucosamine could help to reduce knee joint pain, stiffness, and functional disability of people with osteoarthritis, according to new research published in the top rheumatology journal: Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases.
Combined supplementation with chondroitin sulphate and glucosamine could help to reduce knee joint pain, stiffness, and functional disability of people with osteoarthritis, according to new research published in the top rheumatology journal: Annals of the Rheumatic Diseases. For decades, glucosamine has been used to prevent and treat osteoarthritis. According to a new study that is published in Nutrients, glucosamine supplements may also improve your digestion by counteracting abdominal bloating, constipation, and lumpy stools. It even looks as if glucosamine has other health benefits.
For decades, glucosamine has been used to prevent and treat osteoarthritis. According to a new study that is published in Nutrients, glucosamine supplements may also improve your digestion by counteracting abdominal bloating, constipation, and lumpy stools. It even looks as if glucosamine has other health benefits. Osteoarthritis is a widespread disease that eventually affects the majority of us. The symptoms often feel worse during the wintertime. A European group of experts now recommends glucosamine sulfate as first-line treatment, before painkillers, as glucosamine sulfate is the only remedy that can prevent further progression of the disease and therefore effectively reduces the pain.
Osteoarthritis is a widespread disease that eventually affects the majority of us. The symptoms often feel worse during the wintertime. A European group of experts now recommends glucosamine sulfate as first-line treatment, before painkillers, as glucosamine sulfate is the only remedy that can prevent further progression of the disease and therefore effectively reduces the pain. Increased intake of
Increased intake of  Vitamin D deficiencies are very common. They increase children's risk of developing weak bones, but they also make adults more prone to osteoporosis.
Vitamin D deficiencies are very common. They increase children's risk of developing weak bones, but they also make adults more prone to osteoporosis.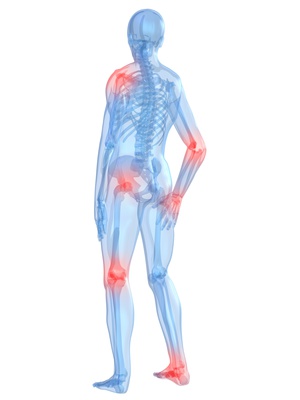 Besides causing pain in joints, osteoarthritis may lead to neck pain, headaches, back pain, tennis elbow, and other symptoms, many of which we normally wouldn't associate with osteoarthritis. It is therefore vital to address the underlying cause. An increasing number of studies show that glucosamine can halt the progression of osteoarthritis and, subsequently, slam the brakes on the accompanying pain. It is, however, important to choose glucosamine in drug form with the type of glucosamine called glucosamine sulfate in order to obtain the desired effect.
Besides causing pain in joints, osteoarthritis may lead to neck pain, headaches, back pain, tennis elbow, and other symptoms, many of which we normally wouldn't associate with osteoarthritis. It is therefore vital to address the underlying cause. An increasing number of studies show that glucosamine can halt the progression of osteoarthritis and, subsequently, slam the brakes on the accompanying pain. It is, however, important to choose glucosamine in drug form with the type of glucosamine called glucosamine sulfate in order to obtain the desired effect. "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.