 Epidemiological studies have led to different results when it comes to vitamin D and its ability to protect against cancer, infections, and various diseases. However, according to a new study published in Cancer Research, this is because magnesium is involved in the activation of vitamin D, on which all cells depend. It therefore does no good to take supplements of vitamin D, if you lack magnesium. And this is exactly the case with many people who eat unhealthy diets, are stressed, use medicine etc.
Epidemiological studies have led to different results when it comes to vitamin D and its ability to protect against cancer, infections, and various diseases. However, according to a new study published in Cancer Research, this is because magnesium is involved in the activation of vitamin D, on which all cells depend. It therefore does no good to take supplements of vitamin D, if you lack magnesium. And this is exactly the case with many people who eat unhealthy diets, are stressed, use medicine etc.
 Sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, certain gastrointestinal infections, and a host of other diseases are so-called autoimmune diseases that occur as a result of the immune defense overreacting and attacking the body’s own tissues. Scientists from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland have now mapped out exactly how vitamin D regulates the immune system. In fact, vitamin D may have a positive effect on autoimmune diseases such as sclerosis. But at our latitude, this provides that we get enough vitamin D from the sun in the summertime and take vitamin D supplements in the winter period. Besides, it is a problem that being overweight both increases the risk of vitamin D deficiency and sclerosis, while lack of magnesium makes it difficult for the body to activate vitamin D.
Sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, certain gastrointestinal infections, and a host of other diseases are so-called autoimmune diseases that occur as a result of the immune defense overreacting and attacking the body’s own tissues. Scientists from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland have now mapped out exactly how vitamin D regulates the immune system. In fact, vitamin D may have a positive effect on autoimmune diseases such as sclerosis. But at our latitude, this provides that we get enough vitamin D from the sun in the summertime and take vitamin D supplements in the winter period. Besides, it is a problem that being overweight both increases the risk of vitamin D deficiency and sclerosis, while lack of magnesium makes it difficult for the body to activate vitamin D.
 Many of us contract respiratory infections during the winter period. In many cases, the underlying cause is a deficiency of vitamin D, a key nutrient for immune health. Vitamin D also regulates the body’s inflammatory response, thereby preventing it from getting out of hand and becoming complicated or life-threatening. In a new review article, researchers looked at vitamin D’s role in preventing and fighting acute respiratory infections such as COVID-19 and influenza with particular focus on children and youngsters. The scientists point out that many people need to take higher doses of vitamin D to optimize levels of the nutrient in their blood.
Many of us contract respiratory infections during the winter period. In many cases, the underlying cause is a deficiency of vitamin D, a key nutrient for immune health. Vitamin D also regulates the body’s inflammatory response, thereby preventing it from getting out of hand and becoming complicated or life-threatening. In a new review article, researchers looked at vitamin D’s role in preventing and fighting acute respiratory infections such as COVID-19 and influenza with particular focus on children and youngsters. The scientists point out that many people need to take higher doses of vitamin D to optimize levels of the nutrient in their blood.
 Vitamin D plays a major role in our health. The main focus, however, is on vitamin D’s importance for bones, while many health professionals are totally unaware of the nutrient’s other essential functions. According to a review article published in Nutrients, half the global population has low vitamin D levels in the blood, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, cancer, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, respiratory infections like COVID-19, and early death. The authors also mention that vitamin D science is often inadequate or misleading because studies focus on supplementation rather than looking at blood levels of 25(OH)D. Consequently, trials are often made with far too small vitamin D doses or with too a short a trial period. In either case, blood levels of vitamin D fail to reach their optimum. What is more, levels of 25(OH)D in the blood should ideally be above 75 nmol/L in order to protect against cardiovascular disease, cancer, and early death. Because this threshold level is higher than the official threshold levels, the scientists recommend high-dosed vitamin D levels as a way to reach an optimal nutrient status.
Vitamin D plays a major role in our health. The main focus, however, is on vitamin D’s importance for bones, while many health professionals are totally unaware of the nutrient’s other essential functions. According to a review article published in Nutrients, half the global population has low vitamin D levels in the blood, which increases the risk of cardiovascular disease, hypertension, cancer, type 2 diabetes, Alzheimer’s disease, respiratory infections like COVID-19, and early death. The authors also mention that vitamin D science is often inadequate or misleading because studies focus on supplementation rather than looking at blood levels of 25(OH)D. Consequently, trials are often made with far too small vitamin D doses or with too a short a trial period. In either case, blood levels of vitamin D fail to reach their optimum. What is more, levels of 25(OH)D in the blood should ideally be above 75 nmol/L in order to protect against cardiovascular disease, cancer, and early death. Because this threshold level is higher than the official threshold levels, the scientists recommend high-dosed vitamin D levels as a way to reach an optimal nutrient status.
 COPD, a lung disease that is primarily a result of smoking, is one of the leading causes of death. Asthma, however, may also become life-threatening if it is left untreated. According to a meta-analysis published in Journal of Global Health, vitamin D supplementation may improve lung function in both diseases. The authors look at how vitamin D strengthens the immune defense and controls inflammation.
COPD, a lung disease that is primarily a result of smoking, is one of the leading causes of death. Asthma, however, may also become life-threatening if it is left untreated. According to a meta-analysis published in Journal of Global Health, vitamin D supplementation may improve lung function in both diseases. The authors look at how vitamin D strengthens the immune defense and controls inflammation.
- which vitamin D2 does not have
 Vitamin D2 occurs naturally in foods from the plant kingdom while vitamin D3 comes from animal sources. It is also vitamin D3 that we synthesize in our skin in response to sun exposure. Scientists from the Universities of Surrey and Brighton in Great Britain have now discovered that the two types of vitamin D have entirely different effects. They therefore sow doubts about vitamin D2’s role in human health, whereas vitamin D3 is known for its vital role in helping the immune system in its fight against infections such as COVID-19. Most cells in the body have vitamin D receptors, and the nutrient is also important for cancer prevention, the nervous system, our mood, and a number of other functions. Vitamin D3 from food, supplements, or sunshine must be activated in the body before it can be utilized.
Vitamin D2 occurs naturally in foods from the plant kingdom while vitamin D3 comes from animal sources. It is also vitamin D3 that we synthesize in our skin in response to sun exposure. Scientists from the Universities of Surrey and Brighton in Great Britain have now discovered that the two types of vitamin D have entirely different effects. They therefore sow doubts about vitamin D2’s role in human health, whereas vitamin D3 is known for its vital role in helping the immune system in its fight against infections such as COVID-19. Most cells in the body have vitamin D receptors, and the nutrient is also important for cancer prevention, the nervous system, our mood, and a number of other functions. Vitamin D3 from food, supplements, or sunshine must be activated in the body before it can be utilized.
 Lack of vitamin D is linked to an increased risk of virus infections, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, dementia, cancer, and osteoporosis. However, the official recommendations for vitamin D intake are way too low, according to two new studies that were presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions in Philadelphia in 2023. In addition, a German study of athletes has shown that it is better to take individually tailored vitamin D supplements to optimize blood levels of the nutrient instead of using a “one-size-fits-all” solution.
Lack of vitamin D is linked to an increased risk of virus infections, respiratory diseases, cardiovascular diseases, dementia, cancer, and osteoporosis. However, the official recommendations for vitamin D intake are way too low, according to two new studies that were presented at the American Heart Association’s Scientific Sessions in Philadelphia in 2023. In addition, a German study of athletes has shown that it is better to take individually tailored vitamin D supplements to optimize blood levels of the nutrient instead of using a “one-size-fits-all” solution.
 Around one billion people worldwide are believed to lack vitamin D. This gives cause for concern when it comes to public health, also with regard to pregnant women and their children. Several studies link vitamin D deficiency to a number of different pregnancy-related complications such as preeclampsia, increased risk of preterm delivery, and the need for a Caesarean section. There is also a risk of low birth weight, weak bones, and later development of bronchitis, asthma, type 1 diabetes, sclerosis, and autism, according to a review article published in Nutrients. The authors believe it is necessary to give supplements to help correct vitamin D deficiencies in the expecting mothers and even in the children after birth to prevent many of the diseases and complications linked to low vitamin D status.
Around one billion people worldwide are believed to lack vitamin D. This gives cause for concern when it comes to public health, also with regard to pregnant women and their children. Several studies link vitamin D deficiency to a number of different pregnancy-related complications such as preeclampsia, increased risk of preterm delivery, and the need for a Caesarean section. There is also a risk of low birth weight, weak bones, and later development of bronchitis, asthma, type 1 diabetes, sclerosis, and autism, according to a review article published in Nutrients. The authors believe it is necessary to give supplements to help correct vitamin D deficiencies in the expecting mothers and even in the children after birth to prevent many of the diseases and complications linked to low vitamin D status.
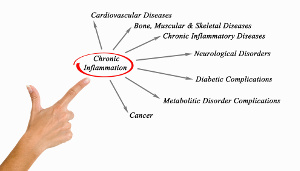 According to WHO, chronic inflammation is the leading cause of death worldwide. Although it is not something that can be felt as such, chronic inflammation sets the stage for a host of different diseases. In a new review article that is published in StatPearls, the authors look closer at why chronic inflammation is so dangerous and how a healthier lifestyle with vitamin D, selenium, magnesium, zinc, and fish oil can help fight the inflammation and prevent the many different diseases and early death that follow in its wake.
According to WHO, chronic inflammation is the leading cause of death worldwide. Although it is not something that can be felt as such, chronic inflammation sets the stage for a host of different diseases. In a new review article that is published in StatPearls, the authors look closer at why chronic inflammation is so dangerous and how a healthier lifestyle with vitamin D, selenium, magnesium, zinc, and fish oil can help fight the inflammation and prevent the many different diseases and early death that follow in its wake.
 The summer sun is our primary source of vitamin D, and previous population studies have suggested that vitamin D may help prevent breast cancer from developing. Danish scientists have looked closer at this relation and found that women from 50 years of age and older who spend a lot of time outdoors – especially between 10 am and 3 pm – have a lower risk of breast cancer. This is important knowledge because it takes years for breast cancer to develop. Vitamin D appears to have a number of different anti-cancer mechanisms, which is why it is vital for us humans to get plenty of the nutrient throughout life.
The summer sun is our primary source of vitamin D, and previous population studies have suggested that vitamin D may help prevent breast cancer from developing. Danish scientists have looked closer at this relation and found that women from 50 years of age and older who spend a lot of time outdoors – especially between 10 am and 3 pm – have a lower risk of breast cancer. This is important knowledge because it takes years for breast cancer to develop. Vitamin D appears to have a number of different anti-cancer mechanisms, which is why it is vital for us humans to get plenty of the nutrient throughout life.
 Decades of intensive farming have depleted the soil. As a result, crops lack up to 40% of their essential nutrients, according to a previously published study from University of Texas and a more recent one from Switzerland. Even if you stick to the official dietary guidelines, you may have difficulty with getting enough calcium, selenium, zinc, iron, vitamin B2, vitamin C, and other essential micronutrients that are required for good health.
Decades of intensive farming have depleted the soil. As a result, crops lack up to 40% of their essential nutrients, according to a previously published study from University of Texas and a more recent one from Switzerland. Even if you stick to the official dietary guidelines, you may have difficulty with getting enough calcium, selenium, zinc, iron, vitamin B2, vitamin C, and other essential micronutrients that are required for good health.
 Zinc is of vital importance to the immune defense, our mental balance, fertility, skin, hair, sense of taste, and numerous other functions. According to a new study that is published in Current Research in Physiology, zincinteracts closely with vitamin D and is important for our cells’ ability to absorb vitamin D. Conversely, vitamin D supports the uptake of zinc in the intestines and supports various zinc-dependent cell functions. According to the new study, lack of one or both nutrients can result in a host of different problems such as infections, poor wound healing, muscle diseases, cardiovascular disease, neurological disorders, osteoporosis, cancer, and many other diseases. This is a problem because zinc and vitamin D deficiencies are rather common – mainly because of unhealthy eating habits, lack of sunlight, ageing, overweight, and the use of certain types of medicine.
Zinc is of vital importance to the immune defense, our mental balance, fertility, skin, hair, sense of taste, and numerous other functions. According to a new study that is published in Current Research in Physiology, zincinteracts closely with vitamin D and is important for our cells’ ability to absorb vitamin D. Conversely, vitamin D supports the uptake of zinc in the intestines and supports various zinc-dependent cell functions. According to the new study, lack of one or both nutrients can result in a host of different problems such as infections, poor wound healing, muscle diseases, cardiovascular disease, neurological disorders, osteoporosis, cancer, and many other diseases. This is a problem because zinc and vitamin D deficiencies are rather common – mainly because of unhealthy eating habits, lack of sunlight, ageing, overweight, and the use of certain types of medicine.
 Epidemiological studies have led to different results when it comes to vitamin D and its ability to protect against cancer, infections, and various diseases. However, according to a new study published in Cancer Research, this is because magnesium is involved in the activation of vitamin D, on which all cells depend. It therefore does no good to take supplements of vitamin D, if you lack magnesium. And this is exactly the case with many people who eat unhealthy diets, are stressed, use medicine etc.
Epidemiological studies have led to different results when it comes to vitamin D and its ability to protect against cancer, infections, and various diseases. However, according to a new study published in Cancer Research, this is because magnesium is involved in the activation of vitamin D, on which all cells depend. It therefore does no good to take supplements of vitamin D, if you lack magnesium. And this is exactly the case with many people who eat unhealthy diets, are stressed, use medicine etc.







 Most people are unaware of vitamin C’s key role in mental health and mood. According to a large population study that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, having higher levels of
Most people are unaware of vitamin C’s key role in mental health and mood. According to a large population study that is published in Frontiers in Nutrition, having higher levels of 


 Sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, certain gastrointestinal infections, and a host of other diseases are so-called autoimmune diseases that occur as a result of the immune defense overreacting and attacking the body’s own tissues. Scientists from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland have now mapped out exactly how
Sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, certain gastrointestinal infections, and a host of other diseases are so-called autoimmune diseases that occur as a result of the immune defense overreacting and attacking the body’s own tissues. Scientists from the University of Edinburgh in Scotland have now mapped out exactly how  Many of us contract respiratory infections during the winter period. In many cases, the underlying cause is a deficiency of
Many of us contract respiratory infections during the winter period. In many cases, the underlying cause is a deficiency of 
 COPD, a lung disease that is primarily a result of smoking, is one of the leading causes of death. Asthma, however, may also become life-threatening if it is left untreated. According to a meta-analysis published in Journal of Global Health,
COPD, a lung disease that is primarily a result of smoking, is one of the leading causes of death. Asthma, however, may also become life-threatening if it is left untreated. According to a meta-analysis published in Journal of Global Health,  Vitamin D2 occurs naturally in foods from the plant kingdom while vitamin D3 comes from animal sources. It is also vitamin D3 that we synthesize in our skin in response to sun exposure. Scientists from the Universities of Surrey and Brighton in Great Britain have now discovered that the two types of
Vitamin D2 occurs naturally in foods from the plant kingdom while vitamin D3 comes from animal sources. It is also vitamin D3 that we synthesize in our skin in response to sun exposure. Scientists from the Universities of Surrey and Brighton in Great Britain have now discovered that the two types of  Lack of
Lack of  Around one billion people worldwide are believed to lack
Around one billion people worldwide are believed to lack  According to WHO, chronic inflammation is the leading cause of death worldwide. Although it is not something that can be felt as such, chronic inflammation sets the stage for a host of different diseases. In a new review article that is published in StatPearls, the authors look closer at why chronic inflammation is so dangerous and how a healthier lifestyle with vitamin D, selenium, magnesium, zinc, and fish oil can help fight the inflammation and prevent the many different diseases and early death that follow in its wake.
According to WHO, chronic inflammation is the leading cause of death worldwide. Although it is not something that can be felt as such, chronic inflammation sets the stage for a host of different diseases. In a new review article that is published in StatPearls, the authors look closer at why chronic inflammation is so dangerous and how a healthier lifestyle with vitamin D, selenium, magnesium, zinc, and fish oil can help fight the inflammation and prevent the many different diseases and early death that follow in its wake. The summer sun is our primary source of
The summer sun is our primary source of  Decades of intensive farming have depleted the soil. As a result, crops lack up to 40% of their essential nutrients, according to a previously published study from University of Texas and a more recent one from Switzerland. Even if you stick to the official dietary guidelines, you may have difficulty with getting enough
Decades of intensive farming have depleted the soil. As a result, crops lack up to 40% of their essential nutrients, according to a previously published study from University of Texas and a more recent one from Switzerland. Even if you stick to the official dietary guidelines, you may have difficulty with getting enough Zinc is of vital importance to the immune defense, our mental balance, fertility, skin, hair, sense of taste, and numerous other functions. According to a new study that is published in Current Research in Physiology,
Zinc is of vital importance to the immune defense, our mental balance, fertility, skin, hair, sense of taste, and numerous other functions. According to a new study that is published in Current Research in Physiology,  "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.