Vitamin D and omega-3 improve mental health by regulating the synthesis of serotonin
 Recent studies reveal that vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids are able to prevent and ameliorate a number of neurological ailments such as depression, ADHD, bipolar disorder, autism, and schizophrenia. There is evidence suggesting that vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids work by controlling the synthesis of serotonin in the brain. The listed neurological conditions are all characterized by defects in the body’s synthesis of this important neurotransmitter. It is therefore vital to get plenty of sunshine, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids, as widespread deficiencies in all three most likely contribute to the increasing rate of different neurological disorders.
Recent studies reveal that vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids are able to prevent and ameliorate a number of neurological ailments such as depression, ADHD, bipolar disorder, autism, and schizophrenia. There is evidence suggesting that vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids work by controlling the synthesis of serotonin in the brain. The listed neurological conditions are all characterized by defects in the body’s synthesis of this important neurotransmitter. It is therefore vital to get plenty of sunshine, vitamin D, and omega-3 fatty acids, as widespread deficiencies in all three most likely contribute to the increasing rate of different neurological disorders.
The brain consists of around 125 billion nerve cells that are connected in a complicated neural network. Information is passed on from one cell to another as electric impulses that travel along the cellular membrane. The actual communication between two adjacent neurons is handled with chemical signaling substances, known as neurotransmitters. There are many different kinds of neurotransmitters, for example serotonin and dopamine. A number of medical drugs and narcotic substances work by either enhancing or inhibiting the effect of neurotransmitters. However, it is preferable to regulate their activity in a more natural way that does not cause side effects or withdrawal symptoms.
| High serotonin levels are associated with | Low serotonin levels are associated with |
| Positive thoughts/ good mood | Negative thoughts/depression |
| Relaxation | Tension |
| Focus and concentration | Excessive thoughts and learning difficulty |
| Normal appetite | Increased hunger |
| Normal relation to stimulants | Increased need for stimulants |
| Normal weight | Overweight |
| Self-control | Impulsiveness |
| High pain threshold | Low pain threshold |
Without enough vitamin D, we are unable to synthesize serotonin
 Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is vital for a host of brain functions and for regulating dopamine levels. We need sufficient amounts of serotonin in the brain in order to have positive thoughts, confidence, and inner rest. A serotonin deficiency increases our risk of negative thoughts, suspicion, depression, irritability, and insomnia.
Serotonin is a neurotransmitter that is vital for a host of brain functions and for regulating dopamine levels. We need sufficient amounts of serotonin in the brain in order to have positive thoughts, confidence, and inner rest. A serotonin deficiency increases our risk of negative thoughts, suspicion, depression, irritability, and insomnia.
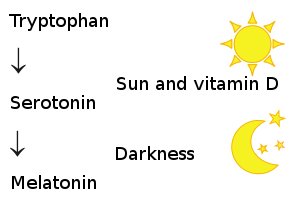
We synthesize serotonin from an amino acid called tryptophan that is found in a variety of foods. In addition, the process requires vitamin D to support enzymatic processes that convert tryptophan into serotonin. Sunlight also enhances serotonin synthesis. First of all, sunlight is our primary vitamin D source. Secondly, sunlight (by way of the retina of the eye) affects our pineal gland’s ability to produce serotonin. When it becomes dark outside, we use a certain amount of serotonin to make melatonin that is highly important for proper sleep.
That way, sunlight and vitamin D are determining factors for enabling the conversion from tryptophan to serotonin, which is then converted into melatonin, a substance that is of vital importance to our mood, 24-hour rhythm, sleep pattern, and general well-being.
Synthesis of and need for vitamin D
When we sunbathe and expose the entire body to sunrays, we are able to synthesis around 100 micrograms of vitamin D in 30 minutes. Sun exposure to the face and hands only enables us to make around 30 micrograms of vitamin D in the same amount of time. This is a much higher amount than the reference intake (RI). In fact, many researchers claim that our actual need for vitamin D is a lot higher than the RI, and their suggestions lie somewhere in the range of 30-100 micrograms daily.
Serotonin does not function optimally without the omega-3 fatty acids, EPA and DHA
While vitamin D supports serotonin synthesis, we also need omega-3 fatty acids to make serotonin function optimally in the brain. The omega-3 fatty acids in question are EPA and DHA that we primarily get from oily fish. However, omega-3 in the form of ALA (alpha-linolenic acid) is also contained in linseed oil and certain other vegetable oils, but many people have difficulty with converting ALA into EPA and DHA due to sluggish enzyme processes. For this reason, the majority of studies is carried out with oily fish and fish oil.
Because DHA is a very long-chained fatty acid, it takes up more space in the individual cell membrane. This contributes to making the cell membrane more pliable and flexible, which is highly important for the cell’s ability to communicate and perform as such. DHA also increases the serotonin sensitivity of serotonin receptors in neurons.
The omega-3 fatty acid, EPA, has anti-inflammatory properties, which is a very useful feature. Recent studies link brain inflammation to a number of neurological disorders like depression and schizophrenia.
Omega-3 fatty acids from fish or supplements?
Dietary guidelines in most countries recommend regular fish consumption, especially oily fish that contain large quantities of EPA and DHA. People who dislike fish or simply find it difficult to eat the recommended amount (300-500 grams per week) may consider taking a fish oil supplement. Fish oil that is based on free fatty acids gives better absorption. It is also important to choose a product that is within the threshold values for peroxides and environmental toxins.
Did you know that a herring fillet contains around 1 gram of omega-3, and a salmon steak contains 3-4 grams of omega-3
Serotonin and SSRI drugs – are they overrated?
There are different views on whether or not serotonin is a “happiness drug”. So far, no studies have shown improvement in depressive patients who are given supplements of L-tryptophan, a precursor of serotonin. However, as this article points out, we also need vitamin D and omega-3 in order to synthesize serotonin and make it work properly.
SSRI drugs (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors) are believed to relieve or reduce depressive symptoms by blocking the serotonin reuptake in certain neurons. However, these anti-depressive drugs have side effects, and many people who take them do not even feel any positive mood changes. This may because they lack vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids, which we humans need in any case for a number of reasons.
Don’t forget stable blood sugar
The brain has a huge energy turnover and is in constant need of blood sugar (glucose). Many people who suffer from depression, ADHD, and other neurological disorders have unstable blood sugar levels. If the brain gets too little fuel, it may affect our serotonin levels. It is therefore always important to have stable blood sugar. A good way to ensure that is by eating coarse, green, and protein-rich main meals with a high content of healthy fats. It may even be a good idea to take organic chromium yeast, because it enhances the effect of insulin that is needed to transport sugar from the blood into our cells.
Did you know that the brain and nervous system primarily use blood sugar (glucose) as fuel, whereas the heart, muscles, and other tissues can also burn fats and protein?
References
University of Queensland. Link Between vitamin D treatment and autism prevention. ScienceDaily 2017
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2017/03/170317131556.htm
UHN staff. Serotonin Deficiency Symptoms That You can Identify Yourself. UHN Daily 2017
http://universityhealthnews.com/daily/depression/7-serotonin-deficiency-symptoms-that-you-can-identify-yourself/
Dr. Dave. Vitamin D and Fish Oil Improve Cognition and Mood by Supporting Serotonin 2016
https://www.integrativepsychiatry.net/blog/vitamin-d-and-fish-oil-improve-cognition-and-mood-by-supporting-serotonin/
Rhonda P Patrick, Bruce N. Ames. Vitamin D and the omega-3 fatty acids control serotonin synthesis and action, part 2: relevance for ADHD, bipolar, schizophrenia, and impulsive behavior. The FASEB Journal 2015
http://www.fasebj.org/content/29/6/2207.abstract
Children’s Hospital & Research Center Oakland. Causal link found between vitamin D-serotonin synthesis and autism in new study. ScienceDaily 2014
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2014/02/140226110836.htm
https://da.wikipedia.org/wiki/Serotonin
Search for more information...
- Created on .








