Vitamin D prevents cancer on several accounts
 - are you getting enough, though?
- are you getting enough, though?
Studies that have been published over the past decades reveal how vitamin D plays an important role in cancer prevention. Studies also show that most of us lack vitamin D. Nonetheless, vitamin D supplements can make a difference, and research suggests that we need more than the official recommendations.
Vitamin D influences most cells and more than 200 genes. The nutrient it considered a very potent hormone that is known to control cell growth and prevent cancer by means of the following mechanisms:
- It inhibits the formation of new blood vessels in tumors (angiogenesis)
- It causes diseased cells to self-destruct (apoptosis)
- It reduces uncontrollable cell division and metastases
- It supports a well-functioning immune defense that is able to destroy cancer cells
- It counteracts local inflammation that is a common trait of many cancer forms
When the body's vitamin D status is low it may affect many of those genes that are responsible for protein coding and the control of cell division. Over time, this may increase your risk of cancer or make it difficult to recover completely after cancer therapy.
More cancers in our sun-deprived, northern part of the world
Sunshine is the single most important source of vitamin D. However, during the winter period the sun sits too low in the sky for humans to be able to synthesize vitamin D, at least in our part of the world. For that reason, we automatically produce far less vitamin D than people in southern countries who get a lot more sunshine.
Way back in the 1940s, researchers discovered a link between UVB exposure from sunlight and cancer mortality. People who lived in the northern hemisphere had an increased risk of Hodgkin's lymphoma and colorectal cancer, breast cancer, and ovary cancer compared with people who lived closer to Equator.
Lack of vitamin D causes cancer
If you have low blood levels of vitamin D, your risk of cancer and early death is increased by 30-40 per cent. This was demonstrated in a large, Danish study that is published in the esteemed British Medical Journal. According to lead investigator Børge Nordestgaard, professor at the University of Copenhagen, a person with vitamin D levels of 33 nmol for every liter of blood (which is 20 nmol below the official recommendation) is 40 per cent more likely to die of cancer.
Skin cancer is on the rise
Despite strong warnings about avoiding the sun and remembering to use sun cream, the rate of skin cancer has not gone down. On the contrary.
Many experts claim that the primary cause of malignant skin cancer (the dangerous kind) is skin traumas such as accidentally cutting into a mole when shaving, or burns from a stove, a sunbed, or the sun. In other words, it is not the sun itself that it is the problem but the traumas/burns. Interestingly, many scientists assume that the sun, which is the primary source of vitamin D, actually protects against the dangerous type of skin cancer - as long as we expose ourselves to healthy amounts of sunshine without getting burned.
Colon cancer
A comprehensive European study has demonstrated a link between low blood levels of vitamin D (less than 50 nmol per liter) and an increased risk of colon cancer. At the same time, people with higher levels of vitamin D in their blood were 40 per cent less likely to develop intestinal cancer.
Breast cancer
Women who expose themselves to a lot of sunshine are only half as likely to develop breast cancer as those who get little sunshine.
Another study divided 1,179 postmenopausal women into three groups. One group got "dummy pills" (placebo), another got a calcium tablet, and the third group got tablets with calcium and vitamin D. The women were monitored for four years. During that period the scientists observed 20 cases of cancer in the placebo group, 17 cases of cancer in the calcium group, and 13 cases of cancer in the vitamin D plus calcium group.
Long-term shift work and working night shifts also increases the risk of breast cancer. This may be a result of low vitamin D and lack of the natural "sleep hormone" melatonin that works as a powerful antioxidant.
| 80% reduced risk of breast cancer |
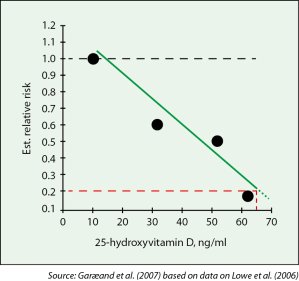 |
| In order to maximize the potential for cancer prevention, one must increase serum levels of vitamin D to at least 40-60 ng/ml (100-150 nmol/L) or more. For breast cancer specifically, the levels must be 80 ng/ml (200 nmol/L) |
Alarming vitamin D deficiency
A recent study conducted on employees from a travel agency showed that nearly half of the participants lacked vitamin D. The National Food Institute of Denmark says that 90% of Danes get too little vitamin D from their diet. An Australian study revealed that 58% lacked vitamin D. This is interesting, as it shows that living in a hot climate is no guarantee of adequate vitamin D levels, if you fail to get enough sunshine.
Why do we lack vitamin D?
Vitamin D deficiency has become more widespread through the past decades due to more time spent indoors, fear of the sun, fear of fat, the use of sun factor cream, and long-term use of cholesterol-lowering medicine. Also, older people and dark-skinned individuals have greater difficulty with synthesizing vitamin D in their skin.
New threshold levels require the use of supplements during winter
The lack of vitamin D and the health consequences that this entails appear to be worse than assumed. When measuring levels of vitamin D in the blood the official threshold values are 50 nmol per liter, but leading scientists fear that this is not enough. Instead, they recommend 75-100 nmol per liter to obtain the right levels for optimal disease prevention.
Chief Physician at Hvidovre Hospital, Dr. Jens-Erik Beck Jensen, does not believe that people can obtain these higher levels of vitamin D by following the official dietary guidelines. Actually, more and more researchers recommend daily vitamin D supplementation through the entire winter period.
Vitamin D, supplements, and absorption
Vitamin D is a lipid-soluble vitamin. For that reason, we utilize this nutrient the most effectively when we take small gelatin capsules with vitamin D dissolved in oil. It is completely safe to take strong supplements of vitamin D with e.g. 38 micrograms in each capsule (1-2 capsules daily)
Facts about official recommendations and the increase in cancer rates
Many people who follow the official dietary guidelines, maintain their ideal weight, limit their alcohol intake, exercise, and avoid smoking still develop cancer
According to the Nordic NORDCAN database, the number of cancers will increase by over 50% in the years to follow
Cancer is currently the leading cause of death among people younger than 65 years
Lack of vitamin D is an overlooked factor. Luckily, we can correct this problem with vitamin D supplements.
The same is the case with lack of selenium, another overlooked factor
References
Sundhedsmagasinet på DR - om D-vitamin mangel 18. 01.2016
Densie Webb, PhD, RD: Vitamin D and Cancer - Evidence Suggest This Vital
Nutrient may Cut Risk. Today´s Dietitian. 2012
Grant WB et al. The association of solar ultraviolet (UVB) with reducing risk of cancer: multifactorial ecologic analysis of geographic variation in age-adjusted cancer mortality rates. Anticancer Res 2006
WU K et al. A nested case control study of plasma 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentrations and risk of colorectal cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 2007
Andreas R Raven: langvarigt skifteholdsarbejde giver dobbelt kræftrisiko. Videnskab.dk 2013
https://www.cancer.dk/fagfolk/forebyggelse/sol/hudkraeft/hudkraeft-i-tal/
Search for more information...
- Created on .








