afterLoad (456.34KB) (4.81ms)
afterInitialise (1.27MB) (24.57ms)
afterRoute (870.36KB) (12.61ms)
beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.52KB) (1.03ms)
afterRenderComponent com_tags (1.46MB) (73.55ms)
afterDispatch (27.78KB) (4.46ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (388.12KB) (9.75ms)
Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (56.7KB) (3.62ms)
After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (2.31ms)
Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (19μs)
After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (42μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (5.08KB) (124ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (4.81KB) (36μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (3.07KB) (61.45ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (816B) (36μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (4.86KB) (260μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (752B) (14μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.67KB) (27μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (608B) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (928B) (22μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (19μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.02KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (720B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.02KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (8μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (245.53KB) (4.25ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (960B) (1.08ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (7μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (70μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (19μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (2.19KB) (32μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (30μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (21.32KB) (380μs)
afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (42μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (5.17KB) (14μs)
afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (25μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.17KB) (11μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.3KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (368B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (224B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.27KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (336B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.25KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (20.94KB) (1.55ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (152.66KB) (2.55ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (720B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (4.36KB) (1.07ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.44KB) (21μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (26.76KB) (3.15ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (12μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (214.16KB) (5.02ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (5.79KB) (34μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (144μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.67KB) (3.03ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (52μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.07KB) (106μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.8KB) (1.69ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (720B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (1.25KB) (52μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (19μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (1.7ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (4μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (35μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (524μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (4μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (45μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (179μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (154μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (24μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (80μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (94μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (733μs)
afterRender (253.71KB) (8.96ms)
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (5.08KB) (34.18%) | 124.17ms |
| 1 x afterRenderComponent com_tags (1.46MB) (20.25%) | 73.55ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (3.07KB) (16.92%) | 61.45ms |
| 1 x afterInitialise (1.27MB) (6.76%) | 24.57ms |
| 1 x afterRoute (870.36KB) (3.47%) | 12.61ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (388.12KB) (2.68%) | 9.75ms |
| 1 x afterRender (253.71KB) (2.47%) | 8.96ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (214.16KB) (1.38%) | 5.02ms |
| 1 x afterLoad (456.34KB) (1.33%) | 4.81ms |
| 1 x afterDispatch (27.78KB) (1.23%) | 4.46ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (245.53KB) (1.17%) | 4.25ms |
| 1 x Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (56.7KB) (1%) | 3.62ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (26.76KB) (0.87%) | 3.15ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.67KB) (0.83%) | 3.03ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (152.66KB) (0.7%) | 2.55ms |
| 1 x After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (0.64%) | 2.31ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (0.47%) | 1.70ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.8KB) (0.46%) | 1.69ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (20.94KB) (0.43%) | 1.55ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (960B) (0.3%) | 1.08ms |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (4.36KB) (0.29%) | 1.07ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderComponent com_tags (20.52KB) (0.28%) | 1.03ms |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (0.2%) | 733μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.29KB) (0.14%) | 524μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (21.32KB) (0.1%) | 380μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (4.86KB) (0.07%) | 260μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (0.05%) | 179μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (0.04%) | 154μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (0.04%) | 144μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.07KB) (0.03%) | 106μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (0.03%) | 94μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (0.02%) | 80μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (0.02%) | 70μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (0.01%) | 52μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 52μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (0.01%) | 45μs |
| 1 x After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (0.01%) | 42μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 42μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (4.81KB) (0.01%) | 36μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (816B) (0.01%) | 36μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 35μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (5.79KB) (0.01%) | 34μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (2.19KB) (0.01%) | 32μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.67KB) (0.01%) | 27μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 25μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (0.01%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (928B) (0.01%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 22μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.44KB) (0.01%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.27KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (0.01%) | 20μs |
| 1 x Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (0.01%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.02KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.02KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (752B) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (5.17KB) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 3 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (608B) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.17KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (720B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (720B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (368B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (224B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (336B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (0%) | 7μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (0%) | 6μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (0%) | 4μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (0%) | 2μs |
 Apparently so. According to a new study published in the journal Alzheimer’s and Dementia, older people who take a daily multivitamin supplement for several years are far less likely to develop dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and other types of cognitive decline. The new study supports earlier research where it has been seen that the different vitamins and minerals increase cerebral blood flow and protect neurons. It pays off to choose high-quality supplements to make sure that the nutrients are properly absorbed in the body.
Apparently so. According to a new study published in the journal Alzheimer’s and Dementia, older people who take a daily multivitamin supplement for several years are far less likely to develop dementia, Alzheimer’s disease, and other types of cognitive decline. The new study supports earlier research where it has been seen that the different vitamins and minerals increase cerebral blood flow and protect neurons. It pays off to choose high-quality supplements to make sure that the nutrients are properly absorbed in the body.







 Everyone is affected by electromagnetic radiation from cell phones, device screens, the electricity supply and other electric systems. The brain’s neurons are particularly vulnerable, especially because electromagnetic radiation can increase the neuronal uptake of calcium ions, which makes the neurons overactive and may even cause them to perish. A study published in News Medical Life Sciences shows that too much calcium in the brain increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and digital dementia in young individuals. The increased electromagnetic radiation also generates loads of free radicals in the body that can cause oxidative stress and cellular damage because it outperforms the body’s different antioxidants. This was described in an article published in The Journal of Microscopy & Ultrastructure that also mentions how electromagnetic radiation can cause stress, headaches, fatigue, anxiety, and other symptoms.
Everyone is affected by electromagnetic radiation from cell phones, device screens, the electricity supply and other electric systems. The brain’s neurons are particularly vulnerable, especially because electromagnetic radiation can increase the neuronal uptake of calcium ions, which makes the neurons overactive and may even cause them to perish. A study published in News Medical Life Sciences shows that too much calcium in the brain increases the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and digital dementia in young individuals. The increased electromagnetic radiation also generates loads of free radicals in the body that can cause oxidative stress and cellular damage because it outperforms the body’s different antioxidants. This was described in an article published in The Journal of Microscopy & Ultrastructure that also mentions how electromagnetic radiation can cause stress, headaches, fatigue, anxiety, and other symptoms.
 The majority of sexually active people contract HPV (human papilloma virus), of which there are several types. Normally, the infection goes away by itself but in some cases it becomes chronic. This increases the risk of serious cell changes in the cervix which, in worst case, can result in cervical cancer. An American study has found that having adequate levels of five different antioxidants – albumin plus vitamins A, B2, E, and folic acid – may lower papilloma virus infections that are linked to cervical cancer.
The majority of sexually active people contract HPV (human papilloma virus), of which there are several types. Normally, the infection goes away by itself but in some cases it becomes chronic. This increases the risk of serious cell changes in the cervix which, in worst case, can result in cervical cancer. An American study has found that having adequate levels of five different antioxidants – albumin plus vitamins A, B2, E, and folic acid – may lower papilloma virus infections that are linked to cervical cancer.
 It is commonly known that pregnant diabetics have an increased risk of developing an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. The diet plays a major role and it appears that a vitamin C deficiency increases the risk, according to a Danish study of pregnant type 1 diabetics that is published in the journal Antioxidants. The authors also mention that vitamin C is a vital antioxidant that protects cells and tissues against oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
It is commonly known that pregnant diabetics have an increased risk of developing an eye disease called diabetic retinopathy. The diet plays a major role and it appears that a vitamin C deficiency increases the risk, according to a Danish study of pregnant type 1 diabetics that is published in the journal Antioxidants. The authors also mention that vitamin C is a vital antioxidant that protects cells and tissues against oxidative stress caused by free radicals. In the summertime, we synthesize vitamin D in our skin when we expose ourselves to sunlight. Vitamin D is a nutrient that is of vital importance to mood and health in general. When it is dark outside, we produce melatonin, which is important for our sleep. In addition to that, melatonin has a number of other important functions. Over the past decades, science has focused on its potential in the prevention of cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, sclerosis, and several other diseases. Apparently, vitamin D and melatonin work as hormones day and night and are of vital importance to the immune system. Also, they regulate inflammation, protect cells, and have many other functions. In a new review article that is published in Nutrients, the scientists refer to melatonin as the “next vitamin D”. Also, they mention that many people get too little sunlight during the day and too little darkness at night, which results in a deficiency of both vitamin D and melatonin.
In the summertime, we synthesize vitamin D in our skin when we expose ourselves to sunlight. Vitamin D is a nutrient that is of vital importance to mood and health in general. When it is dark outside, we produce melatonin, which is important for our sleep. In addition to that, melatonin has a number of other important functions. Over the past decades, science has focused on its potential in the prevention of cancer, Alzheimer’s disease, sclerosis, and several other diseases. Apparently, vitamin D and melatonin work as hormones day and night and are of vital importance to the immune system. Also, they regulate inflammation, protect cells, and have many other functions. In a new review article that is published in Nutrients, the scientists refer to melatonin as the “next vitamin D”. Also, they mention that many people get too little sunlight during the day and too little darkness at night, which results in a deficiency of both vitamin D and melatonin.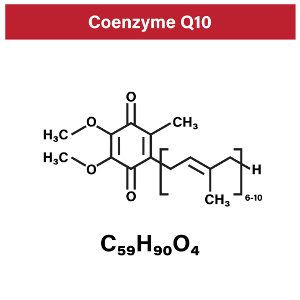 The body uses inflammation as part of its normal immune response to infections and tissue damage. If inflammation becomes chronic, however, it can be extremely dangerous. What happens is that it bombards the body with free radicals. This leads to oxidative stress and increases the risk of cell damage, overweight, and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, and different cancer forms. Diet and lifestyle play a major role, and according to a meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Pharmacology, Q10 supplementation can lower several markers of inflammation and oxidative stress.
The body uses inflammation as part of its normal immune response to infections and tissue damage. If inflammation becomes chronic, however, it can be extremely dangerous. What happens is that it bombards the body with free radicals. This leads to oxidative stress and increases the risk of cell damage, overweight, and chronic diseases like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, autoimmune diseases, and different cancer forms. Diet and lifestyle play a major role, and according to a meta-analysis published in Frontiers in Pharmacology, Q10 supplementation can lower several markers of inflammation and oxidative stress. There is a growing interest among scientists in selenium’s role in the brain and nervous system, and a placebo-controlled study published in Frontiers in Nutrition shows that selenium supplementation is useful as an adjuvant in migraine therapy. The study authors describe that oxidative stress may involved in migraine attacks and mention that selenium has a protective effect due to its role as an antioxidant. Earlier studies have shown that other antioxidants like Q10 and magnesium also have a therapeutic value by way of other mechanisms that may work synergistically.
There is a growing interest among scientists in selenium’s role in the brain and nervous system, and a placebo-controlled study published in Frontiers in Nutrition shows that selenium supplementation is useful as an adjuvant in migraine therapy. The study authors describe that oxidative stress may involved in migraine attacks and mention that selenium has a protective effect due to its role as an antioxidant. Earlier studies have shown that other antioxidants like Q10 and magnesium also have a therapeutic value by way of other mechanisms that may work synergistically.
 Both physical traumas and critical illnesses are associated with inflammation and oxidative stress where free radicals can cause potentially life-threatening damage to cells and tissues. Traumas are estimated to be the cause of one in ten deaths. New research suggests that early intervention with selenium may shorten the hospital stay including the days spent in intensive care and reduce total mortality. This was shown in a study published in Frontiers in Nutrition where the researchers looked closer at selenium’s unique antioxidant properties and anti-inflammatory effect.
Both physical traumas and critical illnesses are associated with inflammation and oxidative stress where free radicals can cause potentially life-threatening damage to cells and tissues. Traumas are estimated to be the cause of one in ten deaths. New research suggests that early intervention with selenium may shorten the hospital stay including the days spent in intensive care and reduce total mortality. This was shown in a study published in Frontiers in Nutrition where the researchers looked closer at selenium’s unique antioxidant properties and anti-inflammatory effect.
 "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.