afterLoad (456.39KB) (494μs)
afterInitialise (1.27MB) (93.24ms)
afterRoute (870.38KB) (35.5ms)
beforeRenderComponent com_tags (21.16KB) (261μs)
afterRenderComponent com_tags (1.92MB) (313ms)
afterDispatch (27.03KB) (11.45ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (373.47KB) (29.64ms)
Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (56.7KB) (1.6ms)
After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (699μs)
Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (16μs)
After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (51μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (5.25KB) (237ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (4.81KB) (30μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.86KB) (112ms)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (816B) (32μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (4.86KB) (234μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (752B) (14μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.67KB) (27μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (608B) (10μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (928B) (21μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.02KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (720B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.02KB) (18μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (19μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (245.53KB) (9.69ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (960B) (58μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (60μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (13μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (2.19KB) (24μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (2μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (30μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (21.32KB) (4.54ms)
afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (64μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (5.17KB) (16μs)
afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (28μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.17KB) (12μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.3KB) (23μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (368B) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (224B) (10μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.27KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (336B) (8μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.25KB) (21μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (9μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (20μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (20.94KB) (557μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (158.16KB) (10.52ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (720B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (4.36KB) (61μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.44KB) (20μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (26.82KB) (14.03ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (22μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (11μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (214.16KB) (14.51ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (5.79KB) (37μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (147μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.7KB) (1.21ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (53μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.07KB) (1.43ms)
afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.8KB) (2.25ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (720B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (1.25KB) (38μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (14μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (2.5ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (5μs)
afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (37μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (9μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.25KB) (561μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (4μs)
afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (45μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (182μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (142μs)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (3μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (24μs)
beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (80μs)
afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (2.74ms)
beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (6μs)
afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (33μs)
afterRender (390.99KB) (15.12ms)
| 1 x afterRenderComponent com_tags (1.92MB) (34.1%) | 312.62ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (5.25KB) (25.8%) | 236.59ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.86KB) (12.17%) | 111.56ms |
| 1 x afterInitialise (1.27MB) (10.17%) | 93.24ms |
| 1 x afterRoute (870.38KB) (3.87%) | 35.50ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (373.47KB) (3.23%) | 29.64ms |
| 1 x afterRender (390.99KB) (1.65%) | 15.12ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (214.16KB) (1.58%) | 14.51ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (26.82KB) (1.53%) | 14.03ms |
| 1 x afterDispatch (27.03KB) (1.25%) | 11.45ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (158.16KB) (1.15%) | 10.52ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (245.53KB) (1.06%) | 9.69ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (21.32KB) (0.5%) | 4.54ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (896B) (0.3%) | 2.74ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (3.89KB) (0.27%) | 2.50ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.8KB) (0.25%) | 2.25ms |
| 1 x Before Access::preloadComponents (all components) (56.7KB) (0.17%) | 1.60ms |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (5.07KB) (0.16%) | 1.43ms |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (22.7KB) (0.13%) | 1.21ms |
| 1 x After Access::preloadComponents (all components) (103.05KB) (0.08%) | 699μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.25KB) (0.06%) | 561μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (20.94KB) (0.06%) | 557μs |
| 1 x afterLoad (456.39KB) (0.05%) | 494μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderComponent com_tags (21.16KB) (0.03%) | 261μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (4.86KB) (0.03%) | 234μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (8.66KB) (0.02%) | 182μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (6.62KB) (0.02%) | 147μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom () (904B) (0.02%) | 142μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom () (688B) (0.01%) | 80μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_articles_category (READ MORE...) (1.25KB) (0.01%) | 64μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (4.36KB) (0.01%) | 61μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (1.3KB) (0.01%) | 60μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (960B) (0.01%) | 58μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (1.23KB) (0.01%) | 53μs |
| 1 x After Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (7.05KB) (0.01%) | 51μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (1.23KB) (0%) | 45μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (1.25KB) (0%) | 38μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_finder () (5.79KB) (0%) | 37μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (1.27KB) (0%) | 37μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.71KB) (0%) | 33μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (816B) (0%) | 32μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (4.81KB) (0%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (1.28KB) (0%) | 30μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (1.27KB) (0%) | 28μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.67KB) (0%) | 27μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (2.19KB) (0%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom () (2.43KB) (0%) | 24μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.3KB) (0%) | 23μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (1.3KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (5.31KB) (0%) | 22μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.27KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (928B) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.28KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.25KB) (0%) | 21μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (1.28KB) (0%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (1.28KB) (0%) | 20μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (3.44KB) (0%) | 20μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (944B) (0%) | 19μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (1.03KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (1.02KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x afterRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (1.02KB) (0%) | 18μs |
| 1 x Before Access::getAssetRules (id:8 name:com_content) (840B) (0%) | 16μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_tags_popular (Search) (5.17KB) (0%) | 16μs |
| 3 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom () (704B) (0%) | 15μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (752B) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (912B) (0%) | 14μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (368B) (0%) | 13μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Remember to download Heart Healthy Seniors) (1.17KB) (0%) | 12μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (6.34KB) (0%) | 11μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (608B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Get additionel and more detailed knowledge ) (368B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (BOOST YOUR IMMUNE DEFENSE) (224B) (0%) | 10μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (736B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Exercise) (720B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (752B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Check this before you buy a Q10 product) (352B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_menu (Main menu-US) (720B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 2 x beforeRenderModule mod_finder () (704B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (720B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Antiaging) (336B) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderRawModule mod_finder () (2.3KB) (0%) | 9μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Are you taking supplements) (352B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Exercise) (336B) (0%) | 8μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Chronic fatigue tied Alan to his bed but Q10 capsules saved him:) (768B) (0%) | 5μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift) (720B) (0%) | 5μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_languages (Sprogskift Mobil) (720B) (0%) | 5μs |
| 1 x beforeRenderModule mod_custom (Cholesterol-lowering without side effects:) (752B) (0%) | 2μs |
 A new British study that is published in British Journal of Nutrition shows that getting too little vitamin D during pregnancy has a negative effect on the social development and motor skills of the toddler. Vitamin D is believed to play a role in brain development. It is vital for the pregnant mother to pay careful attention to getting enough vitamin D all year round, as our modern lifestyle with indoor activities, our frequent use of sunscreen with high sun factor, being overweight, and having dark skin contribute to the widespread deficiency of this nutrient.
A new British study that is published in British Journal of Nutrition shows that getting too little vitamin D during pregnancy has a negative effect on the social development and motor skills of the toddler. Vitamin D is believed to play a role in brain development. It is vital for the pregnant mother to pay careful attention to getting enough vitamin D all year round, as our modern lifestyle with indoor activities, our frequent use of sunscreen with high sun factor, being overweight, and having dark skin contribute to the widespread deficiency of this nutrient.







 It is estimated that one billion people worldwide lack selenium. This has fatal consequences for public health because it increases the risk of virus infections, thyroid disorders, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, neurological disorders, and involuntary infertility. Adding to that problem is the fact that mercury, a known environmental toxin, throws a wrench into selenium’s different functions. In the following, we have compiled a long list of studies that look closer at the consequences of selenium deficiency and the advantage of optimizing the body’s selenium status with help from supplements.
It is estimated that one billion people worldwide lack selenium. This has fatal consequences for public health because it increases the risk of virus infections, thyroid disorders, cardiovascular diseases, cancer, neurological disorders, and involuntary infertility. Adding to that problem is the fact that mercury, a known environmental toxin, throws a wrench into selenium’s different functions. In the following, we have compiled a long list of studies that look closer at the consequences of selenium deficiency and the advantage of optimizing the body’s selenium status with help from supplements.
 Many young men have poor sperm quality and the underlying cause is often unknown. The health of sperm cells depends a lot on omega-3 but a large number of men lack these essential fatty acids. Fish oil supplements have been shown to improve several sperm parameters, according to a large Danish study that is published in JAMA. The scientists behind the study suggest that men may benefit from taking fish oil supplements to improve their fertility and increase the odds of successful conception. However, they also point out that it typically takes one to two months for the optimal effect to show, and you must continue taking the fish oil supplement to maintain the results.
Many young men have poor sperm quality and the underlying cause is often unknown. The health of sperm cells depends a lot on omega-3 but a large number of men lack these essential fatty acids. Fish oil supplements have been shown to improve several sperm parameters, according to a large Danish study that is published in JAMA. The scientists behind the study suggest that men may benefit from taking fish oil supplements to improve their fertility and increase the odds of successful conception. However, they also point out that it typically takes one to two months for the optimal effect to show, and you must continue taking the fish oil supplement to maintain the results. There are several reasons why pregnant women have an increased need for folic acid. Overweight women should even pay special attention, as folic acid reduces their risk of having babies who are also overweight. This was seen in a new American study that got published in JAMA Pediatrics.
There are several reasons why pregnant women have an increased need for folic acid. Overweight women should even pay special attention, as folic acid reduces their risk of having babies who are also overweight. This was seen in a new American study that got published in JAMA Pediatrics. Folic acid plays a role in tissue growth and fetal development during pregnancy. A new study that was presented at an annual congress for British psychologists in Brighton shows that folic acid supplements may even improve the child’s psychological development. This is vital for the child’s ability to handle his or her own feelings and managing socially.
Folic acid plays a role in tissue growth and fetal development during pregnancy. A new study that was presented at an annual congress for British psychologists in Brighton shows that folic acid supplements may even improve the child’s psychological development. This is vital for the child’s ability to handle his or her own feelings and managing socially. Lack of selenium increases the risk of impaired fertility and complications in connection with pregnancy and birth. Because selenium deficiencies are rather common, both men and women should ideally make sure that they get enough of this essential trace element that is involved in various functions - right from conception to delivery.
Lack of selenium increases the risk of impaired fertility and complications in connection with pregnancy and birth. Because selenium deficiencies are rather common, both men and women should ideally make sure that they get enough of this essential trace element that is involved in various functions - right from conception to delivery. A team of scientists from Oregon State University in the United States has managed to explain why lack of vitamin E may cause neurological damage to the developing fetus, and why it increases the risk of spontaneous miscarriage. Their study is published in the science journal Free Radical Biology and Medicine and here, the scientists underline how important it is for both women who are pregnant and those plan pregnancy to get enough vitamin E.
A team of scientists from Oregon State University in the United States has managed to explain why lack of vitamin E may cause neurological damage to the developing fetus, and why it increases the risk of spontaneous miscarriage. Their study is published in the science journal Free Radical Biology and Medicine and here, the scientists underline how important it is for both women who are pregnant and those plan pregnancy to get enough vitamin E. Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the leading cause of infertility and hormone disturbances in women of childbearing age. The condition is often a result of insulin resistance, an imbalance in the sugar metabolism that is typically accompanied by fatigue, abdominal obesity (apple-shaped body), overweight, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and type-2 diabetes. It makes perfect sense to stick with a blood sugar-stabilizing diet and to include a chromium supplement that increases insulin sensitivity and helps, indirectly, regulate the hormone balance. As a bonus effect, it becomes a lot easier to obtain and maintain your ideal weight.
Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is the leading cause of infertility and hormone disturbances in women of childbearing age. The condition is often a result of insulin resistance, an imbalance in the sugar metabolism that is typically accompanied by fatigue, abdominal obesity (apple-shaped body), overweight, and an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and type-2 diabetes. It makes perfect sense to stick with a blood sugar-stabilizing diet and to include a chromium supplement that increases insulin sensitivity and helps, indirectly, regulate the hormone balance. As a bonus effect, it becomes a lot easier to obtain and maintain your ideal weight. Impaired fertility and involuntary childlessness are common in the Nordic countries and there can be a number of reasons for these serious problems. However, according to a large Finnish study that is published in Nutrients, vitamin D deficiency, which is a widespread problem, may increase women’s risk of fertility problems and cause them to have a miscarriage.
Impaired fertility and involuntary childlessness are common in the Nordic countries and there can be a number of reasons for these serious problems. However, according to a large Finnish study that is published in Nutrients, vitamin D deficiency, which is a widespread problem, may increase women’s risk of fertility problems and cause them to have a miscarriage. Approximately one in seven couple is childless. Although there can be many underlying causes, poor sperm quality is an increasing problem. It may be caused by a lack of certain nutrients and exposure to different environmental factors, but, fortunately, it possible to improve sperm quality and increase the chances of conception by means of relevant dietary adjustments and the use of specific supplements. New research shows that epigenetic factors (factors that affect the environment of the sperm cell) determine sperm health and are therefore crucial for activating the genes of the sperm cell so the fetus can develop.
Approximately one in seven couple is childless. Although there can be many underlying causes, poor sperm quality is an increasing problem. It may be caused by a lack of certain nutrients and exposure to different environmental factors, but, fortunately, it possible to improve sperm quality and increase the chances of conception by means of relevant dietary adjustments and the use of specific supplements. New research shows that epigenetic factors (factors that affect the environment of the sperm cell) determine sperm health and are therefore crucial for activating the genes of the sperm cell so the fetus can develop. It is important for the health of the unborn child that the expecting mother keeps her vitamin D levels high during her entire pregnancy. According to a study from Southampton University, vitamin D supplementation is less effective, if a pregnant woman starts with low levels of vitamin D in the early stage of her pregnancy, has major and sudden weight gain, and gives birth during winter.
It is important for the health of the unborn child that the expecting mother keeps her vitamin D levels high during her entire pregnancy. According to a study from Southampton University, vitamin D supplementation is less effective, if a pregnant woman starts with low levels of vitamin D in the early stage of her pregnancy, has major and sudden weight gain, and gives birth during winter.
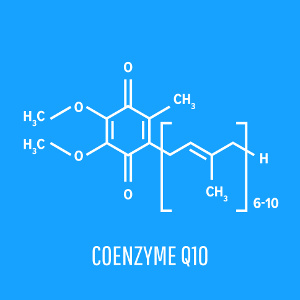 Q10 has a key role in the cellular energy turnover and also serves as an antioxidant that protects the body against oxidative stress. Disruptions in the energy-producing mitochondria in cells and oxidative stress may also be involved in different types of hormone disturbances that affect the thyroid gland, pancreas, sex glands, pituitary gland, and the adrenal glands. In a new review article that is published in Antioxidants, scientists look closer at Q10’s role with particular focus on hyperthyroidism, type 2 diabetes, and poor sperm quality, all of which can be corrected through supplementation.
Q10 has a key role in the cellular energy turnover and also serves as an antioxidant that protects the body against oxidative stress. Disruptions in the energy-producing mitochondria in cells and oxidative stress may also be involved in different types of hormone disturbances that affect the thyroid gland, pancreas, sex glands, pituitary gland, and the adrenal glands. In a new review article that is published in Antioxidants, scientists look closer at Q10’s role with particular focus on hyperthyroidism, type 2 diabetes, and poor sperm quality, all of which can be corrected through supplementation. An international team of researchers has just completed a huge study of the possible link between maternal DNA, selenium deficiency, and preterm labor. Earlier studies have shown that women with low blood selenium have an increased risk of preterm birth and that selenium supplementation may lower that risk. A problem in that respect is that climate changes and soil depletion may increase the risk of selenium deficiencies, especially in Europe.
An international team of researchers has just completed a huge study of the possible link between maternal DNA, selenium deficiency, and preterm labor. Earlier studies have shown that women with low blood selenium have an increased risk of preterm birth and that selenium supplementation may lower that risk. A problem in that respect is that climate changes and soil depletion may increase the risk of selenium deficiencies, especially in Europe.
 Selenium has an overlooked role in sperm quality and healthy pregnancies. A team of scientists from Romania has looked closer at blood levels of different selenium-containing antioxidants and found that low levels are significantly correlated with poor sperm quality. The scientists also explain that lack of selenium increases the risk of pregnancy-related complications, miscarriage, and preterm delivery. Both selenium deficiencies and infertility are common problems so selenium supplementation may be worth considering. For decades, Danish farmers have added selenium to animal fodder as a way of improving the fertility and general health of the animals.
Selenium has an overlooked role in sperm quality and healthy pregnancies. A team of scientists from Romania has looked closer at blood levels of different selenium-containing antioxidants and found that low levels are significantly correlated with poor sperm quality. The scientists also explain that lack of selenium increases the risk of pregnancy-related complications, miscarriage, and preterm delivery. Both selenium deficiencies and infertility are common problems so selenium supplementation may be worth considering. For decades, Danish farmers have added selenium to animal fodder as a way of improving the fertility and general health of the animals. Poor sperm quality, which is a bit of a taboo, is one of the main causes of involuntary infertility. Evidence suggests that Western diets can impair sperm quality, whereas the Mediterranean diet does the opposite. Vegan diets are somewhat controversial, according to a review article published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences. Previous research has shown that supplementation with selenium, zinc, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 can improve sperm cell quality.
Poor sperm quality, which is a bit of a taboo, is one of the main causes of involuntary infertility. Evidence suggests that Western diets can impair sperm quality, whereas the Mediterranean diet does the opposite. Vegan diets are somewhat controversial, according to a review article published in International Journal of Molecular Sciences. Previous research has shown that supplementation with selenium, zinc, fish oil, and coenzyme Q10 can improve sperm cell quality. Hormonal imbalances have broad implications and increase the risk of chronic fatigue, overweight, impaired fertility, dry mucosa, hot flushes, slow metabolism, breast cancer, and many other problems. Lack of essential nutrients contributes to such disruptions of the sensitive hormone system. This is also the case with hormone-disrupting compounds.
Hormonal imbalances have broad implications and increase the risk of chronic fatigue, overweight, impaired fertility, dry mucosa, hot flushes, slow metabolism, breast cancer, and many other problems. Lack of essential nutrients contributes to such disruptions of the sensitive hormone system. This is also the case with hormone-disrupting compounds. Deficiencies of vitamin B12 are widespread due to plant-based diets, aging processes, poor absorption, and certain types of medication. A B12 deficiency can cause anemia, fatigue, poor memory, infections, reduced fertility, impotence, and neurological diseases such as neuropathy, according to an article published in Cureus.
Deficiencies of vitamin B12 are widespread due to plant-based diets, aging processes, poor absorption, and certain types of medication. A B12 deficiency can cause anemia, fatigue, poor memory, infections, reduced fertility, impotence, and neurological diseases such as neuropathy, according to an article published in Cureus. A groundbreaking new Australian study shows that something as simple as a vitamin B3 supplement can prevent miscarriages and congenital defects of the heart and other organs. This is because the nutrient is involved in the body’s production of NAD, a molecule of vital importance to fetal development. Because vitamin B3 deficiencies are common, it is important to have increased focus on the vitamin, especially in connection with pregnancy.
A groundbreaking new Australian study shows that something as simple as a vitamin B3 supplement can prevent miscarriages and congenital defects of the heart and other organs. This is because the nutrient is involved in the body’s production of NAD, a molecule of vital importance to fetal development. Because vitamin B3 deficiencies are common, it is important to have increased focus on the vitamin, especially in connection with pregnancy. In May 2017, new data linking vitamin D and fertility was presented at the European Congress of Endocrinology (ECE) in Lisbon. The new findings contribute to our understanding of vitamin D’s impact on male testosterone levels and of our knowledge about whether vitamin D supplements may actually improve fertility in both sexes. Involuntary infertility, a widespread problem, may be a result of many factors, but if the reason is a vitamin D deficiency, it is easy to treat with increased exposure to sunlight and the use of supplements to keep vitamin D levels optimal all year round.
In May 2017, new data linking vitamin D and fertility was presented at the European Congress of Endocrinology (ECE) in Lisbon. The new findings contribute to our understanding of vitamin D’s impact on male testosterone levels and of our knowledge about whether vitamin D supplements may actually improve fertility in both sexes. Involuntary infertility, a widespread problem, may be a result of many factors, but if the reason is a vitamin D deficiency, it is easy to treat with increased exposure to sunlight and the use of supplements to keep vitamin D levels optimal all year round. Lack of vitamin E increases your risk of fertility problems, atherosclerosis, blood clots, and Alzheimer's disease. The diet contains eight different forms of vitamin E. The vitamin is also available in supplement form, either as natural or synthetic vitamin E, and there are huge differences in terms of their effect.
Lack of vitamin E increases your risk of fertility problems, atherosclerosis, blood clots, and Alzheimer's disease. The diet contains eight different forms of vitamin E. The vitamin is also available in supplement form, either as natural or synthetic vitamin E, and there are huge differences in terms of their effect.
 Even minor zinc deficiencies may cause poor digestion, infections, skin problems, and fatigue – and many other diseases may occur along the way. A new study shows that a diet with as little as four extra mg of zinc daily may strengthen cellular DNA and help protect the body. The four milligrams of zinc are about the same as populations with deficiency symptoms can get by eating zinc-enriched wheat and rice.
Even minor zinc deficiencies may cause poor digestion, infections, skin problems, and fatigue – and many other diseases may occur along the way. A new study shows that a diet with as little as four extra mg of zinc daily may strengthen cellular DNA and help protect the body. The four milligrams of zinc are about the same as populations with deficiency symptoms can get by eating zinc-enriched wheat and rice. "After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child.
"After about one week of taking the Q10 supplement I could feel a huge difference," says 23-year old Alan Piccini, who has been suffering from extreme fatigue and muscle aches ever since he was a child. “Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.
“Taking capsules with co-enzyme Q10 has freed me of the severe side effects of my cholesterol lowering medicine,” Mrs Franken explains.