The Q-symbio study: Large reduction in heart death

Previous studies have shown that patients with heart disease have low levels of Q10 in the heart, and to a low amount of Q10 in the blood is associated with an increased risk of death from heart failure. However, it is only with the Q-symbio study that you can prove a significantly improved survival with Q10 in these patients with sufficiently high confidence.
The Q-symbio study is a high-quality scientific study. It has clearly shown that a daily supplement of Coenzyme Q10 given to patients with severe heart disease can almost halve their risk of dying from heart failure.
The study was led by the famous Danish cardiologist, ass. Professor Svend Aage Mortensen from Copenhagen University Hospital Heart Center in Copenhagen. He says that a significant difference between cardiovascular medicine and Coenzyme Q10 is that heart medicine has the property that it blocks rather than improves cellular processes and that it can have side effects. However, by supplementing with Coenzyme Q10, you use a natural and safe substance that corrects a deficiency in the body and normalizes metabolism in a heart lacking energy without causing side effects.
The Q-symbio study's groundbreaking results were presented to the public at a congress of cardiologists in Lisbon, 23-28th May 2013. The study was the
culmination of a long series of smaller scientific studies that had shown an effect of Coenzyme Q10 against a number of diseases. Q-symbio was a double-blind randomized trial, that was initiated in 2003 with patients from nine countries,Denmark, India, Austria, Poland, Hungary, Slovakia, Sweden, Australia and Malaysia, and published in Journal of the American College of Cardiology.
Biggest study on chronic heart failure and Q10 to date
There are many different types of scientific studies. The different types of studies are ranked according to their quality, ie. their size and level of control. For these reasons scientific studies are weighted differently. At the top we have a type of meta-analyzes, which have systematically collected data from a series of double-blind randomized studies. Slightly lower we find controlled clinical trials, without randomization to determine who gets the active treatment and who gets the placebo. At the bottom we have animal testing and test tube studies. The Q-symbio study is not the only study of high quality that have shown benefit of Coenzyme Q10 for heart patients, but it is the largest and it belongs in the top of the pyramid by being a double-blinded, controlled, randomized trials, and it is also the strongest placebo-controlled Q10 study to date. Double-blind means that neither patients nor researchers know who receive active treatment or dummy placebo before study completion.
When is something scientifically proven?
"Scientifically proven" is not an exact definition. But basically, the effect of a treatment or product must have been proven through scientific experiments of high quality., Ie randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies without flaws. Additionally, there must not have been conducted too many scientific studies with the opposite result. The most conservative circles in medical science will likely require at least two major scientific studies of high quality to be carried out with some 2-3 thousand participants in each study, but often fewer participants will suffice.
The body's energy is created in the mitochondria
M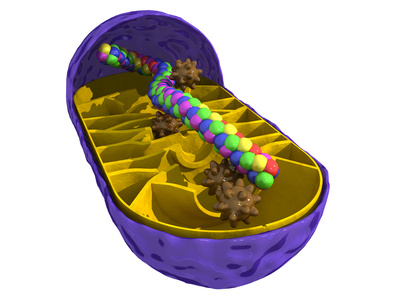 itochondria are tiny cylindrical structures found in almost all cells of the body in varying quantities. They have their own DNA and resembles bacteria. Still, they are indispensable because they act as small power plants which convert the food's nutrients to the energy-rich substance ATP. As much as 90% of the energy available to us we get from our mitochondria, and without Q10 the mitochondria could not produce energy.
itochondria are tiny cylindrical structures found in almost all cells of the body in varying quantities. They have their own DNA and resembles bacteria. Still, they are indispensable because they act as small power plants which convert the food's nutrients to the energy-rich substance ATP. As much as 90% of the energy available to us we get from our mitochondria, and without Q10 the mitochondria could not produce energy.
The more energy a cell needs, the more mitochondria it will contain. The heart muscle is the body's most energy-consuming muscle and therefore it contains the highest number of mitochondria. Each heart cell contains several thousand. Therefore, 1/3 of the heart's dry weight consists of mitochondria. Hair follicles on the other hand contains only a few mitochondria.
The procedure
420 patients from nine different countries with severe heart failure were selected to receive in addition to conventional heart treatment either a Coenzyme Q10, 100 mg capsule* 3 times a day (a total of 300 mg of Q10 daily) or an identical-looking inert placebo capsule, after which the participants in the two groups was followed for two years. The researchers wanted to investigate how long it would take before the participants again experienced problems with the heart.
Heart problems
"Problems with the heart" in this context means an unplanned hospitalization due to heart failure, fatal heart attack, the need for a heart transplantation or the need for a heart-lung machine. The importance of the heart's mitochondria can be illustrated by the fact that approximately 1/3 of the volume of the cardiac muscle is made up by mitochondria.
Since the heart is a particularly energy-demanding muscle, heart cells have the body's highest content of energy-producing mitochondria, all dependent on Q10 to produce the necessary energy.
NYHA classes
NYHA is the abbreviation for the New York Heart Association who developed a simple classification, which is used globally and defines the degree of heart failure in patients. Mortality rates rise and fall in line with the rise or fall of the NYHA class. There are 4 NYHA classes, and the Q-symbio study included only patients with severe heart problems, ie. NYHA III and IV. A successful heart treatment could cause a patient to shift one or more NYHA classes back. E.g. From NYHA IV to NYHA III or II.
NYHA Class I
The weakening of the heart is not felt during normal activity, but can be measured with instruments
NYHA Class II
Shortness of breath and/or fatigue in moderate to harder physical exertion, for example climbing stairs to more than the second floor
NYHA Class III
Shortness of breath and/or fatigue of mild physical exertion such as climbing stairs to less than the second floor or at very modest activity, for example taking clothes off and on
NYHA Class IV
Shortness of breath and/or fatigue at rest
Impressive results
The study showed that patients in the Coenzyme Q10 group had a 43% reduced risk of major, serious cardiac events. There were 30 patients (15%) in the Coenzyme Q10 group who experienced a heart attack, compared with 57 patients (26%) who received dummy capsules (placebo). Supplementation with Coenzyme Q10 also gave a 43% reduced risk of death from all causes compared to the placebo group. All in all, the Coenzyme Q10 treated patients had a clear (significant) reduced cardiovascular mortality, they had significant fewer hospitalizations due to heart failure and substantially fewer side effects than the placebo group. There were also significantly more of the Coenzyme Q10-treated patients who went one or more NYHA classes down (improved their HYHA classification) than in the group receiving placebo. One patient in the Coenzyme Q10 group went from NYHA IV to NYHA I during his treatment.
Diagnosis
 Researchers are able to measure the performance of the heart in several ways. They can eg. measure the amount of NT-proBNP in the blood. It is a hormone-like substance secreted by the heart during chronic strain (heart failure), and is used to predict the risk of a heart attack. The more NT-proBNP found in the blood the harder the heart is strained. It is also possible to measure the percentage amount of blood pumped by the heart with each pulse. This measurement is called the Ejection Fraction (EF). A normal EF is between 55-70%. People with heart failure have an EF of less than 40%. NT proBNB and Ejection Fraction are examples of so-called markers of heart disease that were statiscally improved in the group receiving Coenzyme Q10.
Researchers are able to measure the performance of the heart in several ways. They can eg. measure the amount of NT-proBNP in the blood. It is a hormone-like substance secreted by the heart during chronic strain (heart failure), and is used to predict the risk of a heart attack. The more NT-proBNP found in the blood the harder the heart is strained. It is also possible to measure the percentage amount of blood pumped by the heart with each pulse. This measurement is called the Ejection Fraction (EF). A normal EF is between 55-70%. People with heart failure have an EF of less than 40%. NT proBNB and Ejection Fraction are examples of so-called markers of heart disease that were statiscally improved in the group receiving Coenzyme Q10.
Also healthy people benefit from Coenzyme Q10
The favorable results with Coenzyme Q10 for heart patients has led to Professor Mortensen now recommending that Coenzyme Q10 is added to the standard treatment of heart faliure patients. He adds that it has been many years since a drug has proved able to improve heart patients' mortality. In fact, all kinds of heart disease will at some point lead to heart failure, and the Q symbio study confirms that not only heart patients, but in practice all adults would benefit from Coenzyme Q10.
In other words, Coenzyme Q10 is just as suitable for those who want to maintain a strong heart and a high energy level and thus preventing heart problems as it is to strengthen a weak heart and raise energy levels.
About chronic heart failure
Often heart failure develops over several years, but it can also occur suddenly. When the heart muscle is weakened, its pumping ability is reduced. The consequence is that blood accumulates in the lungs, so you get short of breath and too little blood to the muscles, and you get tired and exhausted.
Symptoms
Shortness of breath, swelling - especially in the legs, "water" in the lungs, fatigue, confusion, forgetfulness, dizziness - especially in the elderly.
European cardiovascular disease statistics 2012
The importance of the Q-symbio study results are best understood when seen in the light of the many cases of cardiovascular disease we are experiencing in Europe. There is both a need for preventive action, and effective tools when the heart has become sick:
- Each year cardiovascular disease (CVD) causes over 4 million deaths in Europe and over 1.9 million deaths in the European Union (EU)
- CVD causes 47% of all deaths in Europe and 40% in the EU
- CVD is the main cause of death in women in all countries of Europe and is the main cause of death in men in all but 6 countries
- Death rates from Coronary Heart Disease (CHD) are generally higher in Central and Eastern Europe than in Northern, Southern and Western Europe
- Death rates from stroke are many times higher in Central and Eastern Europe than in Northern, Southern and Western Europe
- Overall CVD is estimated to cost the EU economy almost ?196 billion a year
- Of the total cost of CVD in the EU, around 54% is due to health care costs, 24% due to productivity losses and 22% due to the informal care of people with CVD
Points to take care of when buying Q10- that the Q10 capsules are produced under pharmaceutical control after drug standardisation - and is able to demonstrate a high bioavailability and safety - that the Q10 content is nature identical. This means that the Q10 molecules in the capsule is completely identical with the Q10 the body produces in a modest amount in the liver - the producer can provide documentation for a high availability, safety and efficacy in the body. Q10 raw material consists of crystals which are not easily absorbed in the body |







